A 3.3 ohm resistor is a low-value resistor commonly use in electronic circuits for current limiting, voltage dropping, and power regulation. This article explores the 3.3Ω axial lead resistor in detail, covering its color codes, types, power ratings, sizes, tolerance, packaging types, and FAQs.
3.3 Ohm Resistor Color Code
Color | 1st Band | 2nd Band | 3rd Band | Multiplier | Tolerance |
Black | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1Ω | – |
Brown | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10Ω | – |
Red | 2 | 2 | 2 | 100Ω | ±2% (G) |
Orange | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1KΩ | – |
Yellow | 4 | 4 | 4 | 10KΩ | – |
Green | 5 | 5 | 5 | 100KΩ | – |
Blue | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1MΩ | – |
Violet | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10MΩ | – |
Grey | 8 | 8 | 8 | 0.001Ω | – |
White | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0.0001Ω | – |
Gold | – | – | – | 0.1Ω | ±5% (J) |
Silver | – | – | – | 0.01Ω | – |
1. 4-Band Color Code (±5% Tolerance - most common):
· Orange – Orange – Gold – Gold
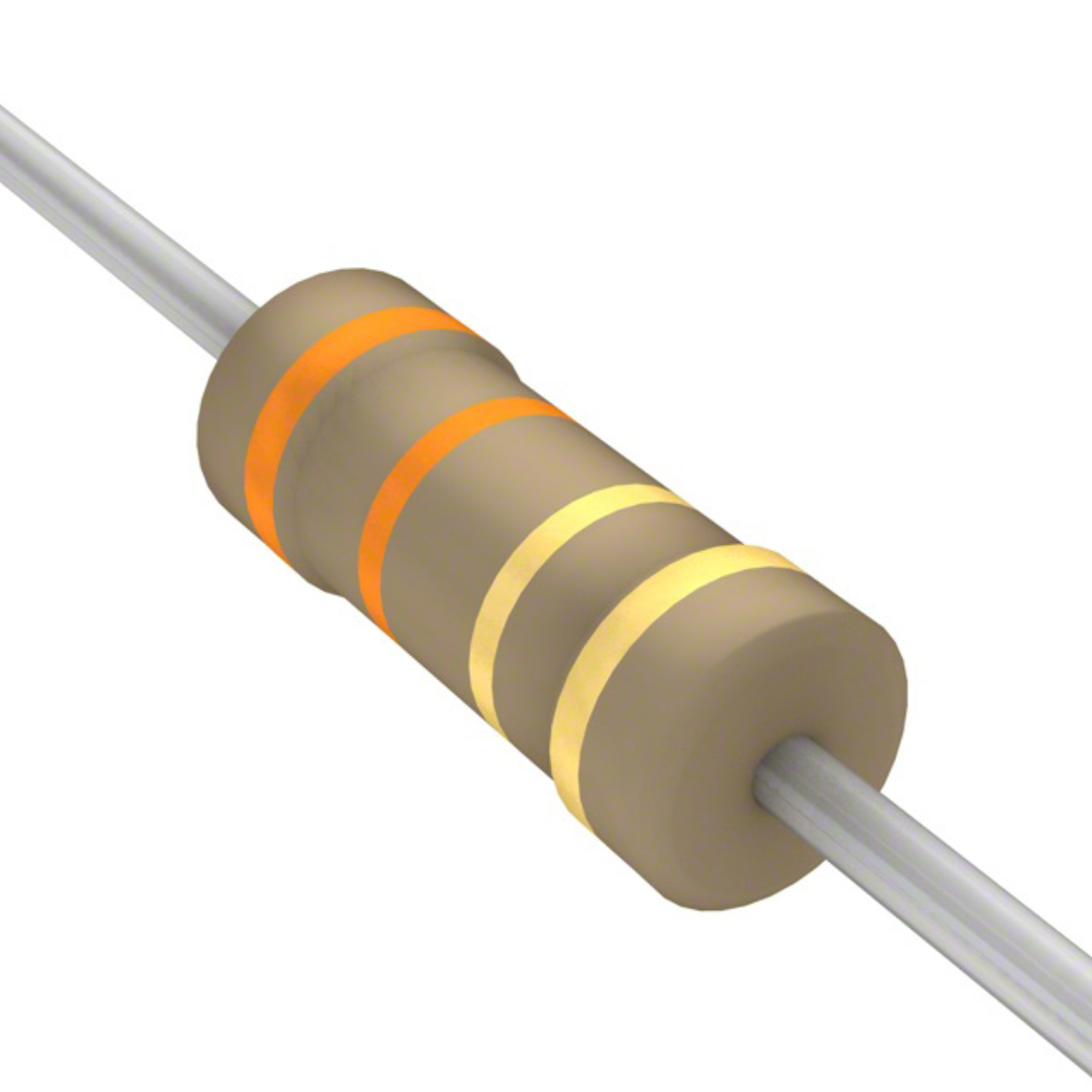
o Orange (1st digit: 3)
o Orange (2nd digit: 3)
o Gold (Multiplier: ×0.1) → 3.3Ω
o Gold (Tolerance: ±5%)
2. 5-Band Color Code (for precision types):
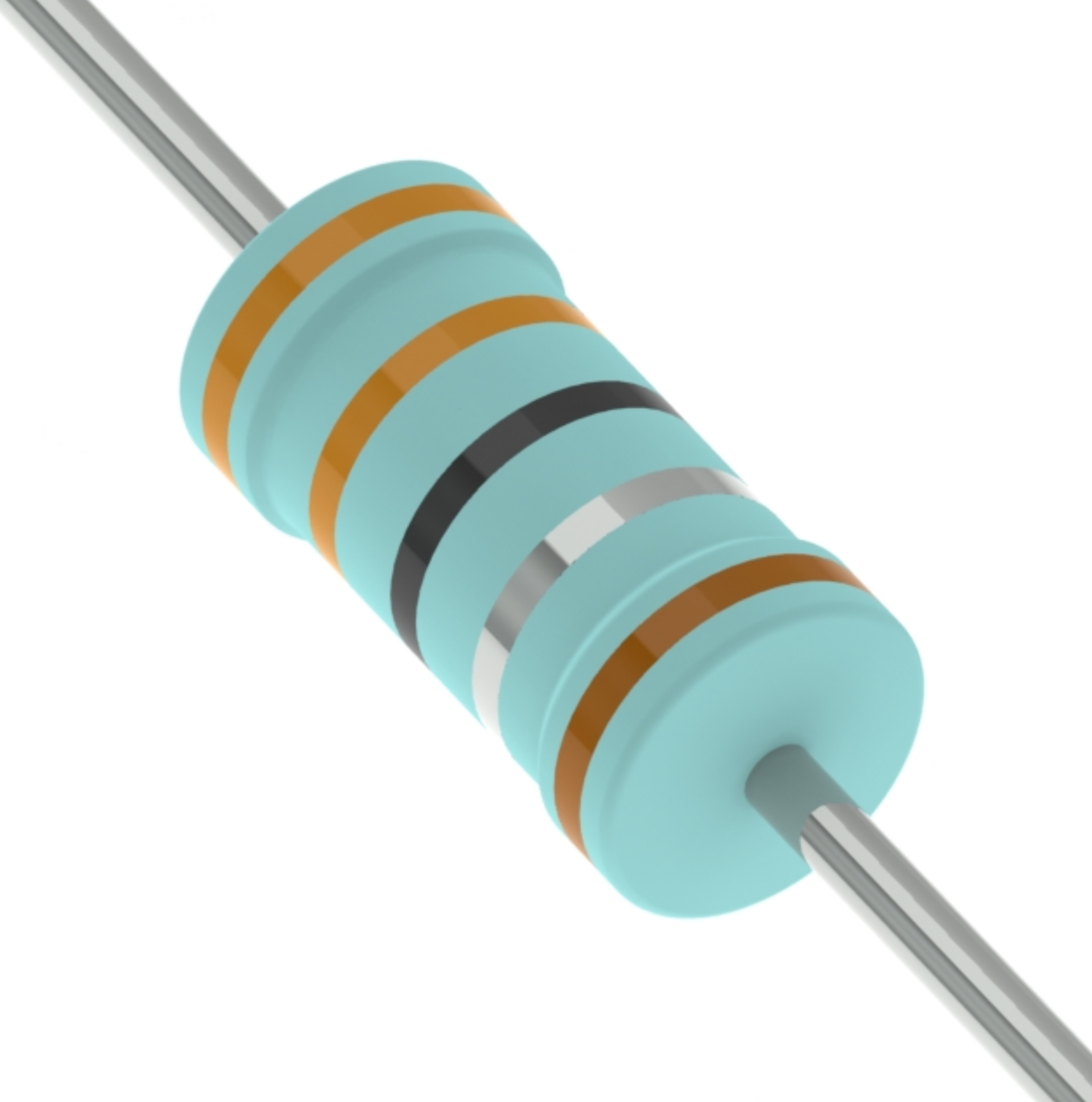
· Orange – Orange – Black – Silver – Brown (±1%)
o Orange (1st digit: 3)
o Orange (2nd digit: 3)
o Black (3rd digit: 0)
o Silver (Multiplier: ×0.01) → 330 × 0.01 = 3.3Ω
o Tolerance (Brown): ±1%
Resistor Types
Different materials and construction types affect the performance, precision, and power handling of the resistor. Here are common types:
Resistor Type | Description |
Carbon Film | Low cost, standard tolerance, general-purpose |
Metal Film | High precision and stability; better temperature coefficient |
Metal Oxide Film | Higher temperature and voltage resistance than metal film |
Thick Film | Make using a thick film technology where a ceramic substrate coat with a resistive material, which then heat to form a durable film. |
Wirewound | High power handling, low noise, precise—use in power circuits |
Power Ratings and Size/Dimension (Axial Lead)
0.063W(1/16W) | 1.5W | 4.5W | 13.5W |
0.125W(1/8W) | 1.75W | 3.3 ohm 5W resistor | 14W |
0.167W(1/6W) | 2W | 5.25W | 15W |
3.3 ohm 1/4 watt resistor | 2.25W | 5.5W | 16W |
0.333W(1/3W) | 2.3W | 6.5W | 20W |
0.4W | 3W | 7W | 25W |
0.5W(1/2W) | 3.25W | 10W | 30W |
0.6W | 3.5W | 11W | 40W |
0.75W(3/4W) | 3.75W | 12W | |
1W | 4W | 13W |
The physical size of a resistor generally increases with power rating. Common axial sizes are:
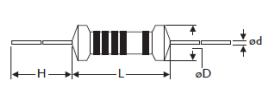
Power Rating | L(mm)± 0.5* ψD(mm)± 0.2 | H(mm) ±2.0 | ψd(mm) ± 0.05 | Common Use Case |
Mini 0.25W (1/4W) 1/8W | 3.4*1.9 | 28 | 0.45 | Low-power circuits, signal conditioning |
Mini 0.5W (1/2W) /(1/4W) | 6.3*2.4 | 28 | 0.55 | General use, breadboards |
1Ws /1/2W | 9.0 *3.3 | 26 | 0.55 | Slightly higher power loads |
3.3 ohm 1 watt resistor | 11.5*4.5 | 35 | 0.8 | Power electronics, audio applications |
2W | 15.5*5.0 | 33 | 0.8 | Industrial or high-power applications |
Tolerance
Tolerance defines how much the actual resistance can vary from the labeled value.
Tolerance | Tolerance Range (Ohms) | Application |
±0.1% | 3.296Ω~3.304Ω | Ultra precision – rare in low ohm |
±1% | 3.267Ω~3.333Ω | Precision applications |
±2% | 3.234Ω~3.366Ω | |
±5% | 3.135Ω~3.465Ω | Standard for general electronics |
±10% | 2.970Ω~3.630Ω | Budget applications |
±20% | 2.640Ω~4.060Ω |
Packing Types
The 3.3Ω resistors available in various packaging :
· Tape & Box – For manual assembly or bulk storage
· Tape & Reel – Suitable for automated insertion machines
· Tray – Typically for high power resistors
· Cut Tape – Small quantity use, like prototyping or repair kits
Frequency Asked Questions
Resistor 3.3 Ohms
1. What color is a 3.3 ohm resistor?
In a 4-band resistor: Orange – Orange – Gold – Gold
3 3-× 0.1(from Gold) =3.3ohms
In a 5-band precision resistor: Orange – Orange – Black – Silver – Brown
3 3 0 -× 0.01(from Silver) =3.3ohms
2. Can I use a higher ohm resistor?
Yes, but it depends on the application, in voltage regulation or current-limiting applications, a higher resistance might be exactly what you need. Here’s how it impacts your circuit:
Always verify with the circuit requirements before substituting.
1. Current Flow
· Higher resistance = Lower current.
· If you use a higher value resistor, less current will flow through the circuit.
2. Component Behavior
· LEDs: A higher resistance will reduce the current flowing through the LED, possibly making it dimmer or not lighting up at all.
· Motors: Higher resistance may result in slower motors or possibly prevent them from starting.
3. Power Dissipation
· A higher resistance resistor will dissipate less power, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
4. Voltage Drop
· Higher resistance will cause a larger voltage drop across the resistor, which might affect other parts of the circuit.
When to Avoid It
· LED circuits: If you need a specific amount of current, a higher resistance might not work because it will reduce the current too much.
· Signal Integrity: In precision signal circuits (like audio amplifiers or digital circuits), altering the resistance can change the signal levels, affecting performance.
3. What is the use of 3.3 ohm resistor?
Commonly use in various applications where need current limiting, voltage regulation, or power dissipation.
1. Current Limiting (Especially for LEDs)
· LED Circuits: Use to limit the current flowing through an LED to prevent it from burning out. For example, if you have a 5V supply and a typical LED with a forward voltage of 2V, a 3.3ohms can help limit the current to an appropriate level (usually around 20mA for standard LEDs).
2. Power Supply and Voltage Regulation
· Voltage Drop: In power supplies, use to drop voltage in a circuit, ensuring that other components receive the correct voltage level.
· Current Limiting in Power Supplies: Use in power regulation circuits to limit the current to specific levels to protect sensitive components.
3. Inrush Current Limiting
· Capacitors and Motors: When circuits with capacitors or motors power on, an initial surge of current (inrush current) can occur. Can help limit this inrush current to avoid damaging components.
4. Snubber Circuits
· In snubber circuits use to suppress voltage spikes, can be part of the network that helps absorb excess energy and protect sensitive components like transistors or diodes.
5. Signal Processing
· Filters: Used in simple RC (resistor-capacitor) filters to smooth out signals, reduce noise, or shape signal waveforms in analog signal processing applications.
6. Power Dissipation in High-Current Circuits
· In high-power applications, use to dissipate heat, control power flow, or balance the load between multiple components.
7. Test Circuits
· Prototyping: 3.3Ω is a common value for testing and prototyping circuits, helping simulate different load conditions and behavior in experimental setups.
8. Feedback Resistors in Amplifiers
· Audio Amplifiers: In some audio circuits or feedback loops, can used as part of the feedback network to adjust the gain or stability of the circuit.
The 3.3 ohm axial lead resistor might seem small, but its applications span from simple LED circuits to complex industrial electronics. Its availability in multiple types, tolerances, and sizes makes it a flexible component in both low- and high-power systems.
Read More:
1.47k Ohm Resistor: color code and Comprehensive Guide
2.10 Ohm Resistor and color code
3.120 Ohm Resistor- Specifications, Applications, and Features
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog