The SS34 diode is a 3A, 40V Schottky diode design primarily for power rectification. Ensuring efficient energy conversion, reducing loss, and protecting sensitive components. Use across industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, renewable energy, and power supplies.
In this article, we will explore the SS34 SMD diode, delve into its features, dimension. And examine common alternatives, equivalent, and testing methods. Whether you're a seasoned electronics engineer or a beginner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to incorporate this chip into your designs.

Key Features of SS34:
· 3A Forward Current: Can handle up to 3A of average current, suitable for mid-range power applications.
· 40V Reverse Voltage: Can use in systems where voltage reversal may occur.
· Low Forward Voltage Drop (~0.5V): This ensures that the diode dissipates less power and reduces energy loss, which is ideal for low-voltage, high-current applications.
· High Efficiency: The fast switching characteristics minimize switching losses, suit for high-frequency circuits.
SS34 Diode equivalent
Other diodes with similar characteristics can use as replacement. Below is a comparison between some of the most common alternatives.
Equivalents Diodes:
Diode | Current Rating | Reverse Voltage | Forward Voltage | Package |
1N5822 | 3A | 40V | ~0.47V | DO-201AD (TH) |
SK34 | 3A | 40V | ~0.5V | DO-214AC (SMA) |
MBR340 | 3A | 40V | ~0.5V | DO-214AC (SMA) |
SS36 | 3A | 60V | ~0.5V | DO-214AC (SMA) |
Key Differences 1N5822 SS34:
· 1N5822 is through-hole, while the SS34 is SMD, suitable for automated assembly.
Here are 3 lists similar part number:
DO-214AC/SMA | |
SK34A-LTP | SS34-HF |
CDBA340-G | SK34A |
B340A-13-F | ACDBA340-HF |
CDBA340-HF | B340A-13 |
B340A-M3/61T | B340AQ-13-F |
SL34A-TP | B340A-E3/61T |
B340A-E3/5AT | B340A-M3/5AT |
VS-30MQ040-M3/5AT | VS-30MQ040HM3/5AT |
SK34AH | APD340VRTR-G1 |
SK34A-TP | CD214A-B340LF |
SK34AHR3G | 15MQ040N |
B340A-13-G-2477 | CDBA340LR-HF |
DO-214AA/SMB | |
B340LB-13-F | STPS340U |
SK34B | B340LB-E3/52T |
SR34_R1_00001 | CDBB340-HF |
SK34SMB | SK34BQ-LTP |
SL34B | SK34BHE3-LTP |
SSB3H40H | SK34BH |
B340BE-13 | B340LB-M3/52T |
SK34SMB-AQ | SL34B-TP |
ACDBB340-HF | CMSH3-40M BK |
CDBB340-G | CD214B-B340LF |
CDBB340LR-HF | B340LB-13-F-2477 |
DO-214AB/SMC | |
VS-MBRS340-M3/9AT | 30BQ040 |
SK34-TP | VS-30BQ040HM3/9AT |
SS34-E3/57T | SS34-M3/57T |
CDBC340-G | SS34HE3_B/H |
SK34_R1_00001 | SSL34 |
ACDBC340-HF | SSC3H40H |
CD214C-B340LF | SS34C-HF |
LSM340JE3/TR13 | 5822SMJ/TR13 |
SS34 size
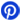
Case | in inches (millimeters) | |||||
L | W | a | H | b | c | |
DO-214AC (SMA) | 0.167±0.01 (4.25±0.25) | 0.098±0.008 (2.5±0.2) | 0.057±0.006 (1.45±0.15) | 0.081±0.006 (2.05±0.15) | 0.047±0.012 (1.2±0.3) | 0.195±0.01 (4.95±0.25) |
DO-214AA (SMB) | 0.172±0.01 (4.38±0.30) | 0.143±0.012 (3.62±0.32) | 0.078±0.007 (2±0.20) | 0.09±0.006 (2.28±0.15) | 0.047±0.012 (1.2±0.3) | 0.21±0.01 (5.33±0.25) |
DO-214AB (SMC) | 0.27±0.01 (6.85±0.25) | 0.23±0.01 (5.90±0.31) | 0.12±0.006 (3.05±0.15) | 0.09±0.012 (2.34±0.28) | 0.047±0.012 (1.2±0.3) | 0.31±0.01 (7.94±0.19) |
Why Choose the SS34 chip?
For various reasons:
· Efficiency in Power Conversion: Its low forward voltage drop of approximately 0.5V makes it more efficient in applications requiring power conversion.
· Reliability: Have high thermal stability and resilience to extreme conditions, making them suitable for use in harsh environments.
· Compact Size: The SMD (Surface-Mount Device) package allows for easy automated placement on printed circuit boards (PCBs), optimizing space in compact designs.
Applications include:
· Power Supplies: It’s use in switching power supplies, ensuring rapid recovery and reduced losses.
· Reverse Polarity Protection: Ensures protection in circuits where incorrect connections could otherwise lead to damage.
· Rectification: In converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Diode SS34 datasheet :
For engineers working with this chip, it’s important to examine its datasheet and understand its specifications in detail.
Key Details:
Parameter | Value |
Maximum Repetitive Reverse Voltage (V_RRM) | 40V |
Average Forward Current (I_F(AV)) | 3A |
Peak Forward Surge Current (I_FSM) | 100A (8.3 ms) |
Forward Voltage (V_F) | 0.5–0.55V @ 3A |
Reverse Leakage Current (I_R) | <500µA @ 40V |
Junction Temperature (T_j) | –55°C to +150°C |
Thermal Resistance (Junction-to-Lead) | ~15°C/W |
Package Type | DO-214AC/SMA |
DO-214AA/SMB | |
DO-214AB/SMC |
Common Applications of SS34
For its attributes, use in various electronic applications, from power supplies to automotive systems. Let’s look at some specific scenarios where it excels:
1. Power Supplies
Use as a rectifier in DC-DC converters and AC-DC converters. In these applications, it helps ensure efficient energy conversion with low power dissipation.
2. Reverse Polarity Protection
Use for reverse polarity protection. When connect in parallel with the power supply, they prevent damage to sensitive electronics by directing current away from components when the polarity reverse.
3. Free-Wheeling Diode
In motor control circuits or inductive loads, it can serve as a free-wheeling diode, protecting the circuit by providing a safe path for the current when the inductive load is turned off.
4. Automotive Electronics
The diode use in various automotive circuits where reverse polarity could damage sensitive components. Use in voltage regulators, battery protection circuits, and charging systems to protect against incorrect connections.
SS34 Diode Test
Testing is a part of the development and troubleshooting process. Here's how you can perform basic testing and diagnostics.
1. Using a Multimeter:
· Set your multimeter to diode mode.
· Place the positive lead on the anode and the negative lead on the cathode.
· You should read a forward voltage of 0.5V to 0.55V.
· Reverse the leads. You should see no reading or “OL” (open loop), indicating the diode is working correctly.
2. Using a Power Supply:
· Forward Voltage (V_F): Connect the diode in series with a current-limiting power supply. Measure the voltage drop across the diode. At 3A, you should get a value close to 0.5V.
· Reverse Leakage Current (I_R): Apply 40V reverse bias to the diode and measure the leakage current, which should be less than 500µA at room temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is SS34 equivalent to?
Similar to SK34, MBR340, and STPS3L40. However, some versions, such as 1N5822, are through-hole diodes and not surface-mount components. Make sure to verify voltage rating, current rating, and package type when choosing an equivalent to ensure compatibility with your design.
2. What is a SS34 diode?
Is a Schottky diode design to handle up to 3A of average forward current and 40V reverse voltage, commonly use for power rectification, reverse polarity protection, and free-wheeling in power electronics. Its key advantages—low forward voltage drop, fast recovery time, and small SMD package—make it a choice in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive systems, and power management.
3. What is the difference between SS54 and SS34?
The SS54 diode is rated for 5A, while the SS34 is rated for 3A.
Summary of Key Differences
Feature | SS34 | SS54 |
Current Rating | 3A | 5A |
Reverse Voltage | 40V | 40V |
Forward Voltage Drop | ~0.5V at 3A | ~0.55V at 5A |
Surge Current Rating | 100A | 150A |
Applications | Low- to medium- power designs | High-power designs |
· SS34: Suit for low- to medium-power applications where space and efficiency are important, such as small power supplies, reverse polarity protection, and DC-DC converters that handle up to 3A.
· SS54: Ideal for higher-power applications that require a 5A current rating and can accommodate a larger package for better thermal dissipation, such as industrial power systems and high-current rectification circuits.
4. What is the difference between SK34 and SS34?
They are electrically similar, with identical current and voltage ratings. The difference is the manufacturer and minor variations in forward voltage.
Summary of Key Differences
Feature | SK34 | SS34 |
Current Rating | 3A | 3A |
Reverse Voltage | 40V | 40V |
Forward Voltage Drop (V_F) | ~0.5V | ~0.5V |
Package Type | SMD | SMD |
Manufacturer | Taiwan Semiconductor (varies) | ON Semiconductor, Vishay, etc. |
Surge Current Rating | 100A | 100A |
Thermal Resistance | ~25°C/W (junction to lead) | ~15°C/W (junction to lead) |
The key differences between them are:
1. Manufacturers: The SK34 is from Taiwan Semiconductor, while the SS34 can come from various manufacturers like ON Semiconductor and Vishay.
2. Thermal Resistance: The SS34 has slightly better thermal resistance, meaning it can dissipate heat more effectively under similar conditions.
In most applications, either diode can use interchangeably, but need to verify the manufacturer's datasheet for specific tolerances and reliability factors. The SS34 prefer in designs where thermal performance is critical, while the SK34 may choose based on availability or price depending on the manufacturer.
5. How big is SS34?
The SS34 is in a DO-214AC (SMA) package, measuring 4.5mm x 3.2mm x 2.8mm.
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog