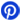
Among the wide range of resistors types available, the 2512 resistor stands out because its specific size, power rating, and applications. Resistors are fundamental components in electrical and electronic circuits, serving to limit the flow of current. In this blog post, we'll explore the details of the 2512 type, here is the catalog.
2. 2512 Resistor Power Rating Wattage and Tolerance
3. 2512 SMD Resistor Datasheet and Resistance Value
5. 2512 Resistor Dimensions, Footprint
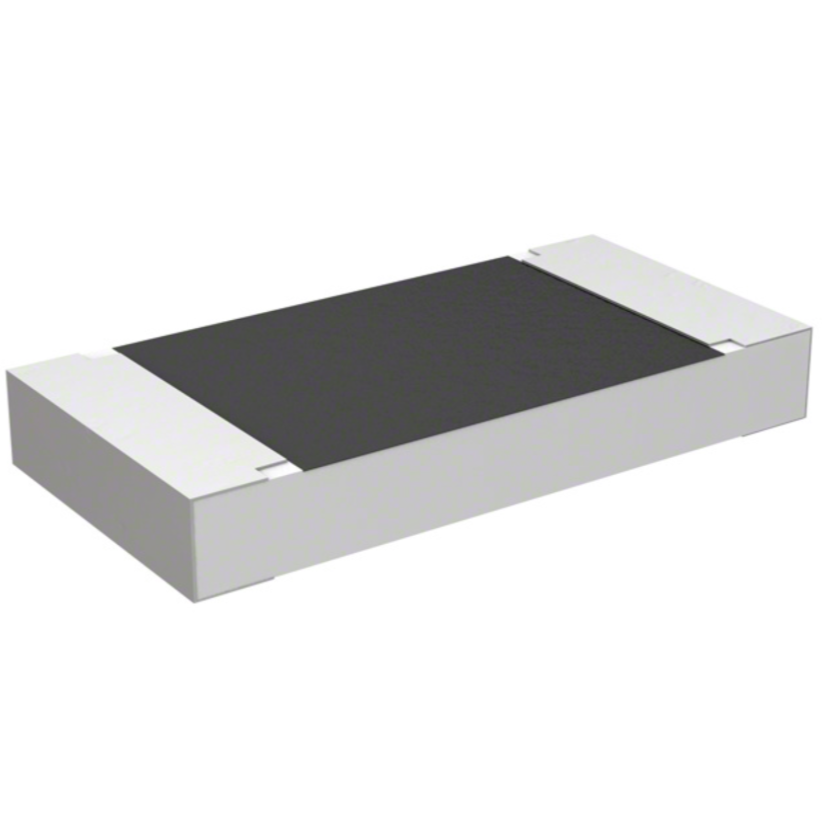

1. What is 2512 Resistor?
Refer to a specific surface-mount device (SMD) resistor with dimensions of 6.3mm x 3.2mm. The numbers in the name "2512" describe the size of the circuit package in imperial measurements, where: 25 represents the length (in hundredths of an inch, so 25 = 0.25 inches or 6.3mm). 12 represents the width (in hundredths of an inch, so 12 = 0.12 inches or 3.2mm).
This size is part of a standardized series of SMD packages, commonly use in modern electronics as their compact form factor, which allows them to fit in space-constrained designs.
Typically use 2512 type for higher power applications compared to smaller SMD sizes such as 0805, 0603 or 0402, as they can handle more power (often ranging from 0.25watts to 3watts, depending on the resistor's specifications). Their size makes them suitable for use in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, power supplies, and other high-power circuits.
2. 2512 Resistor Power Rating Wattage and Tolerance
Determine how much power the circuit can safely dissipate without overheating or failing. 2512 types come in various wattage ratings, making them versatile for different applications.
Here's an overview of the different wattage ratings:
2512 1/2 Watt Resistor
Wattage: 0.5W (500 milliwatts). This is the smallest power rating commonly use in 2512 packages. Suitable for applications where the power dissipation is low, such as signal processing circuits or low-power control systems.
2512 3/4 Watt Resistor
Wattage: 0.75W (750 milliwatts). A slightly higher power ratings, often use this type in circuits where power dissipation is moderate, but still within the low range. Use in some consumer electronics, sensors, and power supplies.
2512 1 Watt Resistor
A standard option for moderate power applications. Use 1W resistors in circuits where the power dissipation is significant but not extreme, such as in amplifiers or small power electronics.
2512 2 Watt Resistor
Wattage: 2W (2,000 milliwatts). Use these in applications that require higher power handling. Typically find in power supply circuits, motor control systems, or high-current applications.
2512 3 Watt Resistor
Wattage: 3W (3,000 milliwatts). With a higher power rating, the 3W resistor is ideal for high-power circuits. They use in high-power applications, such as industrial machinery, automotive systems, and high-current power electronics.
Tolerance Ranges:
Indicate how much the actual resistance can vary from the labeled value. For 2512 types, typical tolerances values include:
±0.01%, ±0.02%, ±0.05%, ±0.1%, ±0.2%, ±0.25%
±0.5%, ±0.85%, ±1%, ±2%, ±3%, ±5%, ±10%, ±20%
2512 0.1% Resistor
Applications: Precision equipment: Use in high-accuracy analog and digital circuits, such as instrumentation, and scientific instruments. High-performance audio systems: Where small deviations can impact the sound quality. Calibration circuits: Use in precision measurement systems. Characteristics: Provides tight tolerance, ensuring minimal deviation in resistance. Commonly use in high-end electronics and research applications where precision is required.
2512 0.5% Resistor
General industrial applications: Widely use in power supplies, automotive systems, and industrial equipment where need moderate precision. Low-power analog circuits: Good for systems where some resistance variation is acceptable, but still requires better accuracy than standard resistors. Consumer electronics: Often use in devices like TVs, radios, or some home appliances. Characteristics: Offers a balance between cost and accuracy, suitable for most precision-sensitive applications but not as tight as 0.1%.
2512 1% Resistor
General-purpose electronics: Common in consumer products like audio devices, automotive electronics, power supplies, and some control systems. Frequently use in designs where exact resistance values are not critical, such as in power dissipation or load circuits. Cost-sensitive projects, when the cost of precision is not justified, 1% tolerance is often a good choice.
Characteristics: The most common tolerance use in everyday circuits. It offers decent accuracy and is cost-effective for many applications.
2512 5% Resistor
Non-critical applications: Use in circuits where not require resistance precision, such as basic power supplies, resistive loads, and general power electronics. Widely find in low-cost consumer electronics, like toys, basic appliances, or simple lighting systems. Use in initial designs and prototype testing where exact resistance is not necessary.
Characteristics: Common for low-cost or bulk production. The higher tolerance allows for cheaper resistors and is acceptable in situations where minor resistance variations don’t affect overall circuit performance.
Higher Precision: A 0.1% tolerance type is typically more expensive than a 5% but require in applications that demand high accuracy.
Cost vs. Performance: For many consumer applications, 1% or 5% tolerance is sufficient, but for mission-critical systems, you would opt for 0.1% or 0.5%. Cost-Sensitive Applications: ±10% or ±20% tolerance types use in low-cost, non-critical systems.
3. 2512 SMD Resistor Datasheet and Resistance Value
The resistance value of a 2512 size is typically available in a wide range, from a few ohms to several megaohms, depending on the application. The datasheet for a 2512 resistor will usually include detailed information on its resistance, power rating, tolerance, temperature coefficient, and more. The value of the resistors usually print in ohms (Ω), and you can determine its application based on its specific resistance.
For example:
Common values: 1Ω, 10Ω, 100Ω, 1KΩ, 10KΩ, 100KΩ, and so on.
Resistance coding: 2512 resistors follow the EIA standard, such as E24 or E96 series, for determining resistance values.
4. 2512 Resistors Type
Different types based on the materials use to create the resistor element. The primary types include:
Metal Film: Known for their accuracy and stability. They widely use in precision applications.
Metal Foil: Offer even higher precision and stability, often use in high-precision circuits.
Thick Film: Made by applying a thick film of resistive material onto a ceramic substrate. They are more cost-effective but less precise than thin-film types.
Thin Film: Make by depositing a thin layer of resistive material. They are more precise than thick film resistors and typically use in high-accuracy applications.
Metal Element: Feature a metal wire or foil as the resistive element. They are highly durable and suitable for high-power applications.
2512 resistors typically pack in Tape & Reel for automated pick-and-place machines. They can also find in cut tape for manual soldering. The Tape & Reel packaging ensures ease of handling and helps improve production efficiency.
5. 2512 Resistor Dimensions, Footprint
A surface-mount device (SMD) with specific dimensions and a corresponding footprint for mounting on a PCB. Here's the detailed breakdown of its dimensions and footprint:
2512 Dimensions | mm | inches |
Length (L) | 6.3 | 0.25 |
Width (W) | 3.2 | 0.12 |
Height (H) | 1.0-1.2 |
The sizes can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer.
Footprint: When designing a PCB for a resistors 2512, it's important to account for the dimensions of both the resistor and its solder pads. The footprint generally includes the dimensions of the pads that will solder to the PCB.
Example Footprint Layout:

Pad/Dimension | Size (mm) |
Pad Length | 4.0 - 4.2 mm |
Pad Width | 2.0 - 2.2 mm |
Pad-to-Pad Distance | 6.3 mm |
Resistor Length | 6.3 mm |
Resistor Width | 3.2 mm |
Footprint Recommendations:
1.Pad Size: The pads should be large enough to allow the solder to make good contact with the resistor’s leads. The pads should generally be 2.0mm to 2.2mm wide, and 4.0mm to 4.2mm long, ensuring good soldering and minimal risk of poor connections.
2.Land Pattern: A land pattern (or footprint) is the area on the PCB where the resistor will sit. The land pattern should match the resistor's length and width so that it can sit comfortably with minimal movement.
3.Clearance: Ensure adequate clearance around the pads for the soldering process, and avoid placing other components too close to the circuit to prevent overheating during soldering.
4.Soldering Considerations: Given the larger size of the 2512 resistor, the soldering process should ensure proper heat dissipation. Commonly use Hot air reflow soldering or wave soldering methods .
Additional Tips for Footprint Design:
Ensure proper thermal management in the PCB design to handle the power dissipation of higher-wattage 2512 resistors.
If the circuit is high-power rated (e.g., 2W or 3W), ensure larger traces or the use of a heat sink for better heat dissipation.
Can use simulation tools to double-check your footprint for correct pad size and distance to ensure a good solder joint.
6. Resistor 2512 Application
Widely use across many industries because their high power rating, compact size, and versatility. They are ideal for application where space is limited but power dissipation is relatively high. Some common applications include:
Can use in voltage regulation circuits, power converters, and battery management systems. In Consumer Electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other devices where compact components are necessary. Use in automotive electronics for power control and regulation. In communication equipment, such as RF circuits, signal processing, and other high-frequency applications. Find in machinery, control systems, and industrial control panels electronics.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
1.How many watts is a 2512 resistor?
Typically come in power rating ranging from 0.5W (1/2 watt) to 3W, depending on the specific model. The most common wattage ratings are 1W and 2W. Design higher wattage resistors in the 2512 package for use in power-sensitive applications, allowing them to dissipate more heat compared to smaller SMD resistors like 0805 or 0603. Wattages rating selection depends on the application and the amount of power the circuit needs to handle without overheating or failing because excessive heat buildup.
2.How big is a 2512 resistor?
The part of the surface-mount device (SMD) package family, with a size of 6.3mm (length) by 3.2mm (width), and a typical height of around 1.0-1.2mm. This makes it significantly larger than smaller SMD packages like 2010, 1812 ,0805 or 0603. The size allows the 2512 resistor to handle higher power ratings, which is why it is often use in circuits requiring higher heat dissipation. Its size also contributes to better tolerance and stability under load, making it suitable for industrial, automotive, and power electronics applications.
3.What is the voltage rating of 2512?
The voltage rating varies depending on factors such as power rating, resistance value, and material construction. Typically, the voltage rating of a 2512 type ranges from 200V to 500V. Higher wattage types in this package can often handle higher voltage, with certain configurations rated up to 1kV for high-power applications. Can calculate the exact voltage rating based on the power ratings and resistance value, ensuring that the resistor will safely operate within its specified limits without causing breakdown or failure.
4.What is the most expensive resistor?
The most expensive resistors tend to be high-precision wirewound resistors or those made from specialized materials like tantalum, nichrome, or platinum. These resistors can have extremely tight tolerances, sometimes as low as ±0.01%, and use in precision applications like aerospace, high-end instrumentation, and scientific research. The cost increases with factors like tolerance, stability, and the use of rare or custom materials. Precision resistors with low temperature coefficients and high stability are also among the most expensive, as they are crucial for applications requiring long-term accuracy.
In conclusion, the 2512 resistor is a necessary component for modern electronics. With its wide range of power ratings, resistance values, and applications, it offers flexibility for designers looking for high-performance resistors in space-constrained or high-power circuits. Whether you’re designing consumer electronics, automotive systems, or industrial equipment, the 2512 resistor is a reliable choice to ensure both power dissipation and compact design.
Read More:
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog