Among different resistance values, the 22K ohm resistor (22 kilo-ohms) is one of the most widely use passive components in electronics. They control current, divide voltages, and provide stability to circuits. Whether you are building a hobby circuit, designing an amplifier, or working on industrial electronics, the 22 K resistor plays a key role.
In this guide, we will cover everything about the 22000 ohms —its definition, types, packages, power ratings, colour codes, datasheet, applications, and FAQs.
1. What is a 22K Ohm Resistor?
4. Common Applications of Resistor 22K Ohm
5. Where to Buy 22K Ohm Resistor and Price?
7. Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ] About 22K Ohm Resistors

What is a 22K Ohm Resistor?
22KΩ-ohm is a fixed-value passive electronic component with a resistance of 22,000 ohms. The letter “K” in its value stands for kilo, meaning 1,000. Therefore, 22K = 22 × 1,000 = 22,000 Ω. The primary function of 22KΩ is to limit current flow and control voltage in an electrical or electronic circuit. By offering resistance to the flow of electrons, it helps protect components, set reference voltages, and stabilize operations.
The 22K-ohm is available in different tolerances (±1%, ±5%, ±10%), power ratings, and package types including through-hole (axial and radial) and SMD (surface-mount device). Depending on the application, it can make from carbon-film, metal-film, wirewound, or metal oxide film.
In practical use, a 22K ohms commonly find in voltage divider networks, biasing-circuits, filters, timing-circuits, and pull-up or pull-down resistor configurations in microcontroller systems. Its widespread availability, low cost, and versatility make it a standard resistance value in electronics. Whether in consumer devices, audio equipment, or industrial control systems, the 22Kilos Ω is an necessary building block for reliable circuit design.
Types of 22K Resistor
Come in different designs, package formats, and technologies. Choosing the right 22K-ohms depends on your project’s power requirements, PCB layout, and accuracy needs.
Through Hole Package Type:
Axial Resistors:

Cylindrical body with color-coded bands and leads extending from both ends. These are the most common types for breadboards, prototyping, and traditional PCB assembly.
Radial Resistors:
Have both leads extending from the same side of the body. They are compact and often use where PCB space is limited, such as in power supplies and consumer electronics.
22K Resistor SMD: A generic surface-mount package that solder directly onto PCB pads.
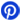
0805 SMD Resistor 22K: Compact (0.08” × 0.05”) size, commonly use in smartphones, computers, and compact electronics.
22K Chip Resistor 1206: Slightly larger (0.12” × 0.06”), allowing for better power handling while still saving space on the PCB.
Resistor Types by Material
Carbon Film: Low-cost, general-purpose, moderate accuracy, use in consumer electronics.
Metal Oxide Film: Provide better thermal stability and are ideal for high-voltage applications.
Wirewound: Made from resistive wire wound around a core, suitable for high-power loads.
22K Metal Film Resistors: High precision (±1% tolerance) and low noise, use in sensitive measurement and audio circuits.
22K Ohm Resistor Array: A package that contains multiple resistors, often use in digital circuits for pull-up/pull-down networks.
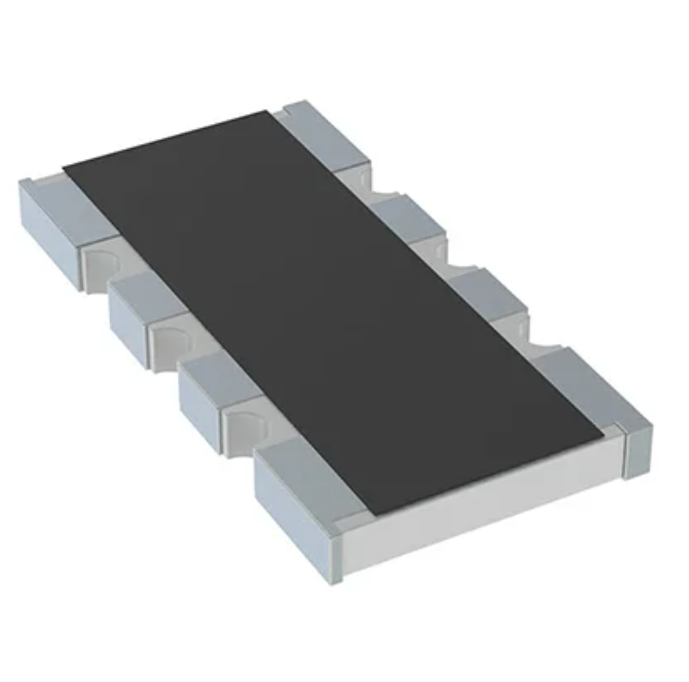
Power Rating Options
Choose with an appropriate power ratings to avoid overheating. The following are the common wattages:
22K Ohm 1/4 Watt Resistor – The most common size, ideal for low-power signal processing circuits.
22K Ohm 1/2 Watt Resistor – Handles more current than the standard 0.25W, good for small amplifiers.
Resistor 22K 2 Watt – Use in medium power applications such as audio systems and regulators.
22K 2.4 Watt Resistor – Provides additional thermal headroom for industrial circuits.
Resistor 22K 3Watt – Rugged design for continuous higher current loads.
22K 4 Watt Resistor – Use in power electronics and heavy-duty consumer devices.
Resistor 22K Ohms 13W – Design for industrial machinery and applications where large amounts of power must dissipate safely.
22K Resistor Color Code
Colors Coding 4 Band:
Band | Colour | Value | Meaning |
1st-Band | Red | 2 | First-digit |
2nd-Band | Red | 2 | Second-digit |
3rd-Band | Orange | ×1,000 | Multiplier |
4th-Band | Gold | ±5% | Tolerance |
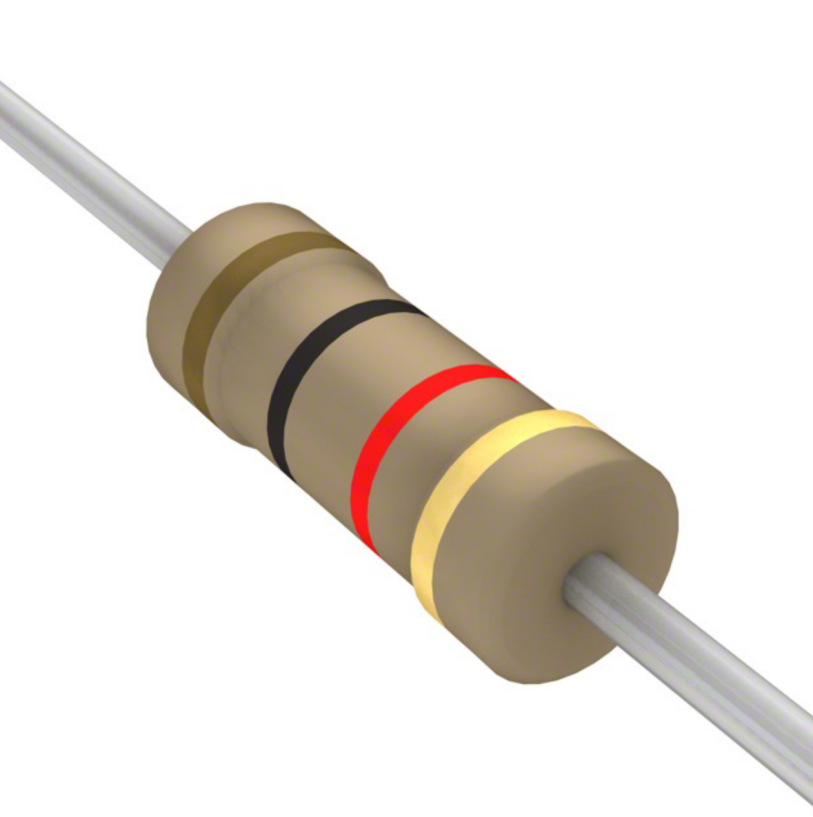
The 4-band 22K ohms has the colors coding: Red – Red – Orange – Gold.
First-Band (Red):The first-digit is 2.
Second-Band (Red):The second-digit is 2.
Third-Band (Orange):This is the multiplier. Orange means ×1,000.
So far: 22 × 1,000 = 22,000 ohms.
Fourth-Band (Gold): This indicates tolerance, meaning the actual resistance can vary ±5% from the marked value.
Final Value = 22,000 Ω (22 K ohms ±5%)
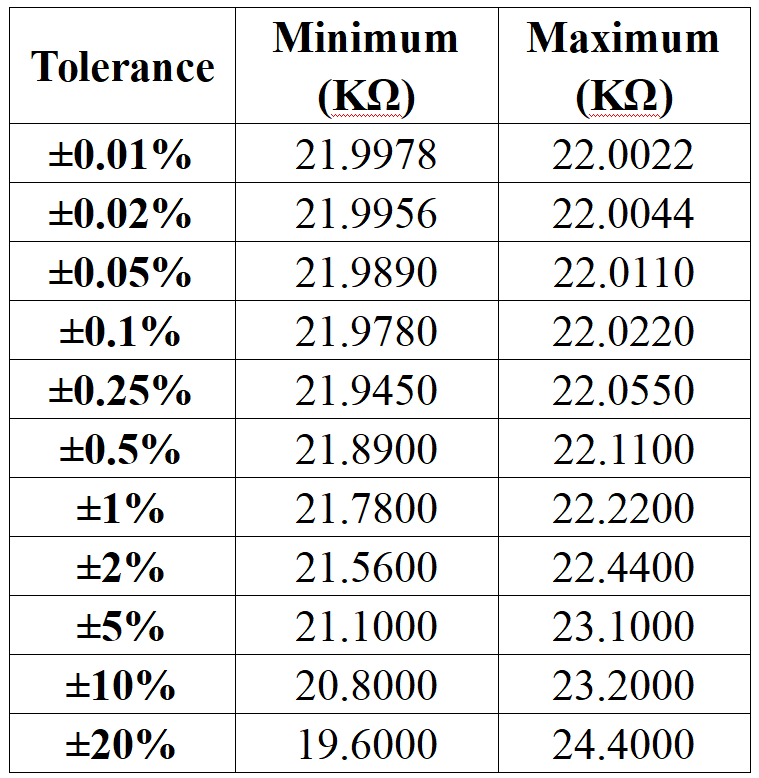
22K Ohm Resistor Color Code 5 Band
Band | Color | Value | Meaning |
1st-Band | Red | 2 | First-digit |
2nd-Band | Red | 2 | Second-digit |
3rd-Band | Black | 0 | Third-digit |
4th-Band | Red | ×100 | Multiplier |
5th-Band | Brown | ±1% | Tolerance |
Final Value = 220 × 100 = 22,000 Ω (22 K ohm ±1%)
To read a 22Kohm five-band with the colour coding Red–Red–Black–Red–Brown, begin by identifying the side with the tolerance band, which is brown. Reading from the opposite end, the first-band is red, which represents the digit 2. The second-band is also red, giving another digit 2. The third-band is black, which represents 0. Putting these three values together gives 220. The fourth-band is red and serves as the multiplier, meaning ×100. When you multiply 220 by 100, the result is 22,000 ohms. The fifth-band is brown, which indicates a tolerance of ±1%. This means the actual resistance can range between 21.78K and 22.22K ohms.
Common Applications of Resistor 22K Ohm
The resistor 22Kilo is one of the most commonly use values in electronics as its versatility and reliability. In voltage divider circuits, the 22 K ohms helps reduce high voltage levels to safe values for microcontrollers, sensors, and other electronic components. Widely use in biasing circuits to set the correct operating point for transistors, FETs, and operational amplifiers, ensuring stable and consistent performance in analog and digital circuits.
In signal processing applications, the 22-K ohms works with capacitors to create RC filters, including low-pass and high-pass filters, which are useful in audio circuits, communication devices, and sensor signal conditioning. In digital electronics, 22000 ohm serve as pull-up or pull-down resistors, maintaining default logic levels on microcontroller pins, digital ICs, and logic gates.
Also use in timing and oscillator circuits, where it controls the charge and discharge of capacitors, setting precise time intervals and frequency in timer ICs and oscillator circuits. Additionally, it use in feedback networks of amplifiers to adjust gain and improve stability.
Thanks to its moderate resistance value, high availability, and low cost, the 22K-ohm widely use in consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial control circuits, and DIY electronics projects, making it a component for both professional engineers and hobbyists.
22K Ohm Resistor Datasheet
Although datasheets vary by manufacturer, a typical data sheet contains the following:
Parameter | Typical Value |
Resistance | 22,000 Ω |
Tolerance | ±1%, ±5%, ±10% |
Power Rating | 1/8W to 13W |
Temperature Coefficient | ±50~±200 ppm/°C |
Maximum Working Voltage | 200 – 500V |
Operating Temperature | -55°C to +155°C |
The datasheet helps engineers select the right resistor based on precision, stability, and thermal performance.
Where to Buy 22K Ohm Resistor and Price
To buy 22KΩ resistors from Orwintech Electronics, you can visit our official website or contact customer support for pricing and availability. Orwintech offers a variety of resistor types, including carbon-film, metal oxide film, metal-film, and SMD resistors with various power ratings and tolerances.
If you are looking for bulk purchases or specific types such as 22K ohm 1W, 1/4W, or high-precision resistors, we have these in stock. You can also inquire about any bulk discounts or specialized orders if needed.
Price Range for 22K Ω
The pricing can vary based on factors like type, tolerance, power rating, and quantity purchased.
Standard Carbon Film(1/4W, ±5%): Approximately US$0.005~0.010 per unit.
Metal Film(1/4W, ±1%): Around US$0.01~0.02 per unit.
High Precision Resistors (0.1% tolerance): Between US$0.020~0.50 per unit.
Power Resistors (1W and above): Typically US$0.050~1.00/unit, depending on specifications.
Bulk purchases often come with discounted rates, so consider your project needs and order accordingly.
22K Ohm Variable Resistor
The variable (also known as a potentiometer or trimpot) is a type of resistor that allows you to adjust its resistance value within a specified range, typically from 0 to 22K ohms. Widely use in voltage control circuits, volume control in audio equipment, and adjustable settings in electronic projects. They consist of a resistive track, a wiper (which moves along the track), and two fixed terminals.
Types of 22K Variable Resistors:
Rotary Potentiometer:
Commonly use for user-adjustable control, such as volume knobs or brightness controls in consumer electronics.
Trimpot:
Smaller and use for fine adjustments during the design phase or in circuits that require infrequent but precise changes.
Slide Potentiometer:
Often use in audio mixing boards or other applications requiring linear adjustment over a specified range.
Parameter | Value |
Resistance Range | 0–22K Ω |
Tolerance | ±10% (typical) |
Power Rating | 0.1W – 1W |
Adjustment Type | Rotary, slide, trimmer |
Mechanical Life | >10,000 cycles |
Applications of 22K Ohm Variable Resistor
1. Volume Control in Audio Systems
In audio equipment, where it serves as a volume control. It allows users to adjust the output signal, effectively controlling the loudness of the sound in devices such as amplifiers, mixers, and radios.
2. Brightness and Contrast Adjustment in Displays
In television sets, computer monitors, and LCD displays, use a 22K potentiometer to adjust brightness or contrast levels. By changing the resistance, the circuit alters the voltage going to the display, enabling users to optimize visibility.
3. Voltage Dividers in Circuits
Use variable resistors in voltage divider circuits where need precise adjustments to the output voltage. It enables fine control over the voltage output by adjusting the resistance, which is necessary for sensor calibration or feedback systems in various electronic devices.
4. Calibration of Circuit Components
In measurement systems and calibration devices, the 22K potentiometer allows for the fine-tuning of a circuit. Use to set specific conditions in oscillators, amplifiers, or filters, ensuring that the circuit works within a desired tolerance or threshold.
5. Adjustable Biasing in Transistor Circuits
In transistor amplifiers, the 22K potentiometer often use for biasing purposes. By adjusting the potentiometer, you can control the current flowing through the transistor, ensuring it operates in its optimal region, which is necessary for amplifier stability and signal clarity.
6. Sensor Sensitivity Adjustment
For sensors or light-dependent resistors (LDRs), use a 22K variable to adjust the sensitivity or the reference voltage. This helps fine-tune the sensor’s response to environmental changes, ensuring accurate readings in home automation systems or robotics.
7. Motor Speed Control
In DC motor control circuits, can the 22K potentiometer to adjust the motor speed. By varying the resistance, can control the voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for smoother speed adjustments in applications such as servo motors, drones, or robotic arms.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ] About 22K Ohm Resistors
What is the color code for 22K ohm resistance?
The 4-band colour codes is Red-Red-Orange-Gold. The first two bands (Red-Red) represent the digits 2-2, giving 22. The third-band (Orange) is the multiplier, representing 1,000. The fourth-band (Gold) indicates a tolerance of ±5%. This results in a total resistance of 22,000 ohms (22Kohm), with a ±5% tolerance. For a 5-band colour code (Red-Red-Black-Red-Brown), the first three bands form 220, the fourth-band is a multiplier of 100, and the fifth-band (Brown) represents ±1% tolerance.
What is a 22K ohm resistor used for?
A 22K ohms resistors use in various electronic circuits, primarily for voltage division in resistor networks. It commonly find in biasing circuits, filter circuits, and feedback loops in amplifiers. In digital electronics, it often use as a pull-up or pull-down resistor for logic circuits. It helps regulate current flow and maintain stable voltages in sensitive components such as transistors, op-amps, and microcontrollers. It also has applications in timing circuits, oscillators, and sensor calibration, where require precise voltage control for reliable circuit behavior.
Can substitute 20K resistor for 22K?
Substituting a 20K for a 22K ohms is generally not recommended unless the tolerance of the circuit allows a small deviation. A 20K has a lower resistance value, which can affect the circuit’s performance, especially in voltage divider networks or biasing circuits where precision is critical. The difference in resistance could lead to inaccurate voltage levels, altered timing intervals, or incorrect biasing of transistors and amplifiers. If the tolerance is tight, it is better to use the correct 22K ohms to maintain circuit reliability and accuracy.
What’s the replacement 22K ohm resistor?
When looking for a replacement for a 22K ohm resistor, ensure that the new circuit has similar power rating, tolerance, and resistors type. Common replacements include metal film resistors, which offer better precision and lower noise than carbon-film types. You can choose with a similar tolerance (e.g., ±5% or ±1%) and the appropriate power rating (e.g., 1/4W, 1/2W, or 1W), depending on your circuit's needs. Ensure the replacement meets the voltage and current specifications to avoid overheating or damaging the circuit.
What does 'k' mean on a resistor?
The letter "k" in a resistor’s value, such as 22K ohms, stands for kilo, which means 1,000. Therefore, a 22K resistors represents 22,000 ohms. This unit of measurement use to simplify resistance values for more manageable representation. The values typically give in ohms (Ω), and the "k" prefix allows for expressing larger resistance, such as 22K (22,000) or 47K (47,000), without needing to write out zeros. Other prefixes such as M (mega) or G (giga) represent even larger values like millions and billions of ohms.
How does a 2k2 resistor relate to a 22k ohm resistor?
A 2K2 resistor (2.2K ohms) is 10 times smaller than a 22K. The “K” represents a multiplier of 1,000, so a 2K2 resistor has a resistance of 2,200ohms, while a 22K resistor has a resistance of 22,000ohms. Although both use in similar applications, such as biasing, voltage division, or signal conditioning, the difference in resistance value means they would behave differently in a circuit. A 2K2 resistor would allow more current to flow than a 22K resistor under the same voltage conditions.
What power rating should I consider when choosing a 22k ohm resistor?
When choosing a 22K ohm resistor, consider the power rating required by your circuit. For most low-power applications, a 1/4W or 1/2W power rating is sufficient. However, for circuits with higher currents or voltages, you need a 1W, 2W, or higher power-rated. The wattage rating is necessary to ensure that the resistor can handle the heat generated by the current passing through it. To calculate the powering ratings, use the formula: P = V² / R, where P is power, V is voltage, and R is resistance.
Conclusion
The 22K ohm resistor is a versatile and key component in electronics. With a resistance of 22,000 ohms, it widely use in voltage dividers, biasing, filtering, and digital circuits. Available in through-hole, SMD, carbon-film, metal-film, wirewound, and variable forms, it caters to different power and precision needs.
By understanding its types, color codes, applications, datasheet parameters, and selection tips, you can choose the right 22K resistor for your project with confidence.
Read More:
1. Complete Guide to 2K Resistor - 2000 Ohm
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog