Among the many resistance values, the 47 ohm resistor is one of the most commonly use as its balance of current-limiting capability, versatility, and availability in many different packages and technologies. Resistors use in almost every circuit, from the simplest LED setup to advanced power supplies, audio systems, and industrial machinery. In this detailed guide, we will explore 47 ohm’s types (through-hole and surface mount), colour codes, data sheet specifications, applications, power rating considerations, and frequently asked questions. By the end of this post, you will have a complete understanding of why the 47 Ω is such a popular choice in the world of electronics.
4. 47 Ohm Resistor Datasheet Key Specifications
5. Applications of 47 Ohms Resistor
6. Selecting the Right Resistor 47 Ohm
7. Frequently Asked Questions About 47 Ohm Resistor
What is a 47 Ohm Resistor?
A passive two-terminal electronic component that resists the flow of electric current by offering a fixed resistance of 47 ohms (Ω). The primary purpose of this circuit is to limit current, divide voltages, bias active components such as transistors, and protect sensitive devices like LEDs from excessive current.
In circuit design, the 47 Ω strikes a balance — it is low enough to allow moderate current flow while still providing protection. This makes it a common choice for current-limiting applications, input/output impedance matching, and load balancing.
Example: If apply a 5.6V supply across a 47 Ω resistor, the current is about 0.12 A (120 mA), as calculated by Ohm’s Law (I = V/R).
Types of 47 Ohm Resistors
Come in different forms depending on 47-ohm’s construction, size, and application. The 47Ω resistor is available in both through-hole and surface mount packages, as well as in different technologies such as carbon, metal film, wirewound, and metal oxide. Below is an in-depth look at each type.
Through-Hole (Axial) Resistors
Cylindrical components with wire leads on both ends, design to insert into holes on a PCB. The 47 ohm axial type is one of the most widely use in hobby electronics and prototyping because it’s easy to solder and identify with its color bands.
Advantages: Easy to handle, color-coded, reliable for manual soldering.
Applications: Audio circuits, simple filters, LED current limiting, educational kits.
47 Ohm Resistor SMD
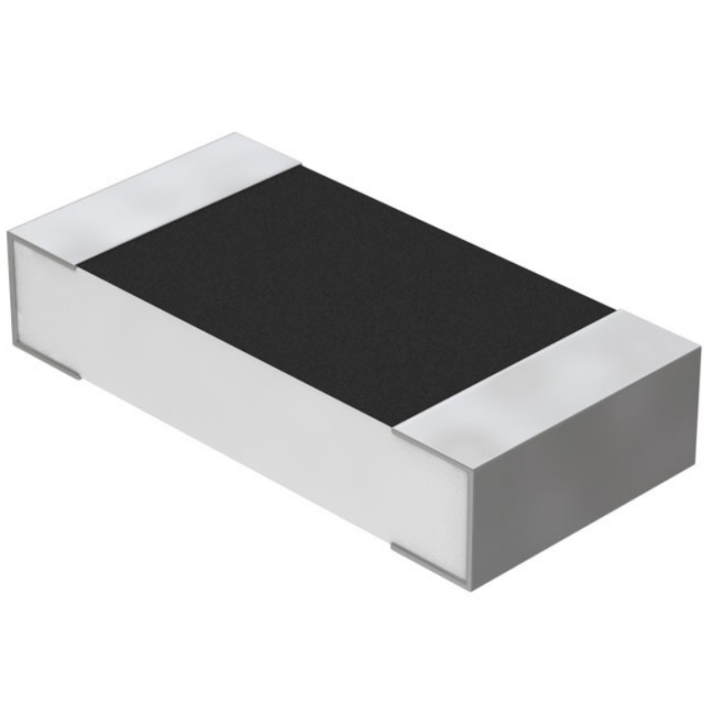

Surface-mount resistors are much smaller than axial ones and solder directly onto the PCB surface. The SMD type prefer in compact, high-density electronics.
47 Ohm SMD Resistor 1/10 Watt
Refers to a surface-mount device (SMD) with a resistance value of 47-ohms and a power rating of 0.1 watts (1/10W). Typically use in low-power applications where heat dissipation is minimal, and space is a concern, as they design to mount directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB) without the need for through-hole mounting.
47 Ohm Resistor 0805 Footprint
The 0805 SMD package means the size measures 0.08 × 0.05 inches (2.0 × 1.25 mm). This is a standard size for low-power resistors, usually up to 1/8W.
Applications: Smartphones, IoT devices, communication boards.
Resistor 47 Ohm 2512
The 2512 package is much larger at 0.25 × 0.12 inches (6.3 × 3.2 mm), allowing higher wattage handling, typically 1–2W.
Applications: Power supplies, high-current sensing, automotive electronics.
Surface Mount 47 Ohm Resistor Array
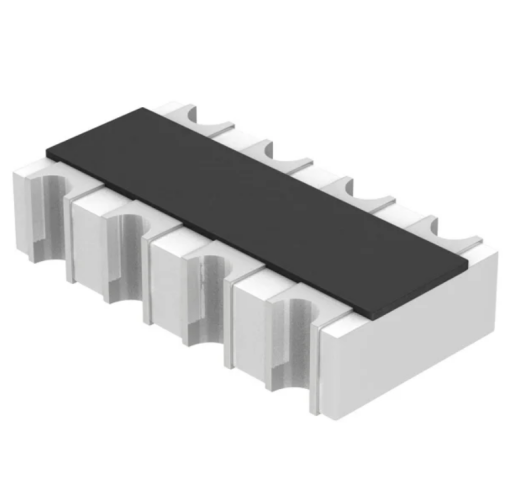
A array combines multiple resistors in a single SMD package. A 47 ohm array saves space and improves reliability.
Applications: Pull-up/pull-down resistor networks, bus termination, data line protection.
Metal Film 47 Ohm Resistors
Made by depositing a thin metal film onto a ceramic rod. They offer high precision, low noise, and better temperature stability than carbon resistors.
Use in audio amplifiers, measuring instruments, medical equipment.
47 Ohm Carbon Resistor
Widely used in the past but are now less common as their high noise and low stability. Use in non-critical hobby projects.
Wirewound Resistor 47 Ohm
Constructed by winding a resistive wire around a ceramic core. They can handle high power dissipation. Use in power supplies, test loads, current limiting in high-voltage circuits.
Metal Oxide Film Resistors
Made with a metal oxide film, giving them better thermal stability and higher surge handling than carbon or metal film.
Advantages: Flameproof, high surge resistance, better for harsh environments.
Applications: Power regulators, surge protection, industrial equipment.
47 Ohm Fusible Resistor
A fusible type acts as both a resistor and a fuse. If excessive current flows, the resistor burns out safely like a fuse, protecting the circuit.
Applications: Power supplies, TV circuits, appliances, over-current protection.
Benefit: Prevents fire hazards compared to standard resistors.
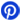
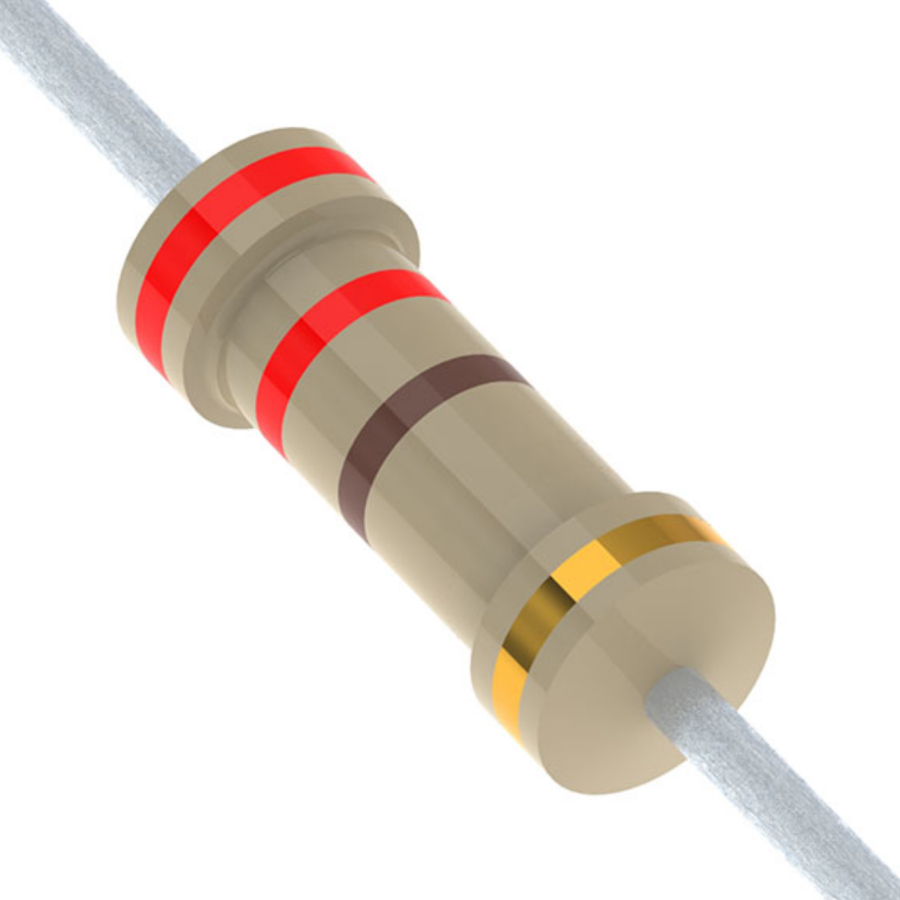
47 Ohm Resistor Color Code
47 Ohm 4 Band Resistor
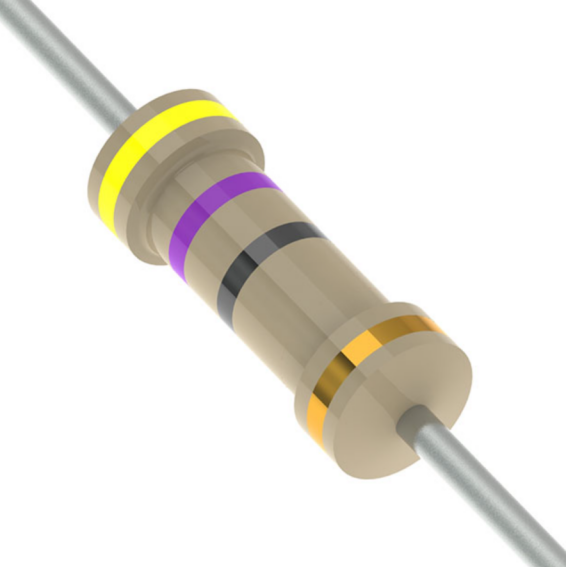

Band 1 (Yellow) represents the first-digit in the resistance value, which is 4. Band-2 (Violet) is the second-digit in the resistance value, which is 7. Band-3 (Black) represents the multiplier or the number of zeros to add. Since black represents x1, no zeros are added. So, 47 ohms is the base value. Band-4 (Gold) is the tolerance band, means the actual resistance can vary by ±5% from the stated value (i.e., from 44.65-ohms to 49.35-ohms).
Band | Color | Meaning |
1 | Yellow | First Digit: 4 |
2 | Violet | Second Digit: 7 |
3 | Black | Multiplier: x1 |
4 | Gold/Brown | Tolerance: ±5%(Gold) or ±1% (Brown) |
Thus, a 47 ohms is with a 4-band colour coding of Yellow (4), Violet (7), Black (x1), Gold (±5%).
47 Ohm Resistor Color Code 5 Band
The 5-band follows a more precise method of encoding the resistance value, which is particularly useful for applications where require higher accuracy.
Band | Colour | Meaning |
1 | Yellow | First Digit: 4 |
2 | Violet | Second Digit: 7 |
3 | Black | Third Digit: 0 |
4 | Gold | Multiplier: x0.1 |
5 | Brown/ Red/ Green / Violet | Tolerance (e.g., ±1%, ±2%, ±0.5%, ±0.1%) |
47 ohm Resistor (5-Band Color Code): Yellow (4), Violet (7), Black (0), Gold (x0.1), Brown (±1%)
First three digits form the value: 4 - 7 - 0. Multiply by the multiplier: 470 × 0.1 = 47 ohms. The tolerance is ±1%, meaning the actual resistance could range from 46.53 to 47.47 ohms.
Why Use the 5-Band Code?
Higher Precision: The 5-band colour codes allows for greater precision in resistance values by encoding an additional digit and using a multiplier for finer scaling. This is particularly useful when dealing with sensitive circuits that require tight resistance tolerances.
Smaller Variance: The multiplier (such as x0.1) enables resistors to achieve lower resistance values (like 47 ohms) with more accuracy than the typical 4-band code.
47 Ohm Resistor Datasheet Key Specifications
Here’s a breakdown of the parameters commonly found in a 47 ohms datasheet:
1. Resistance Value
A 47-ohm restricts current flow and sets the voltage drop in a circuit. Often choose the fixed value of 47 ohms for applications such as LED current limiting, voltage dividers, and impedance matching.
2. Tolerance
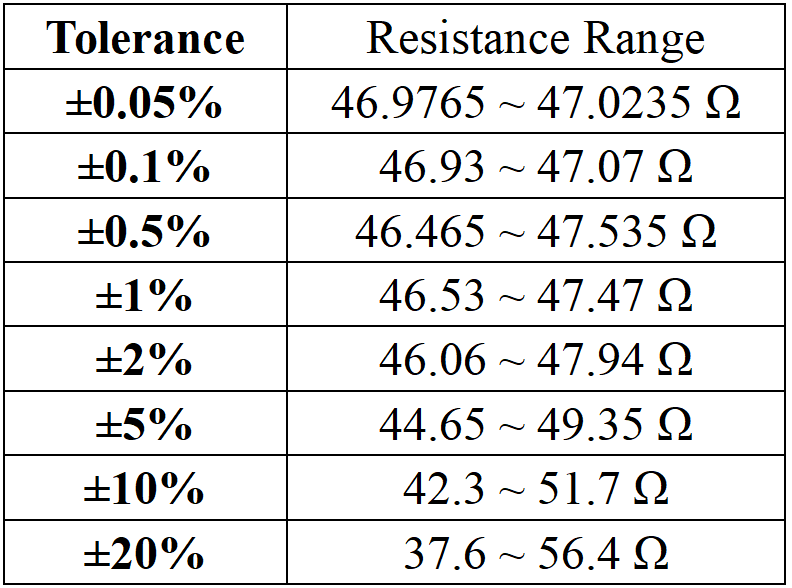
Indicates how much the actual resistance value can vary from the nominal value (47 ohms). For example, a ±5% tolerance means the actual resistance could vary by up to 5% from the nominal value. Higher tolerances such as ±0.5% and ±0.25% are available for more precise applications.
3. Power Rating
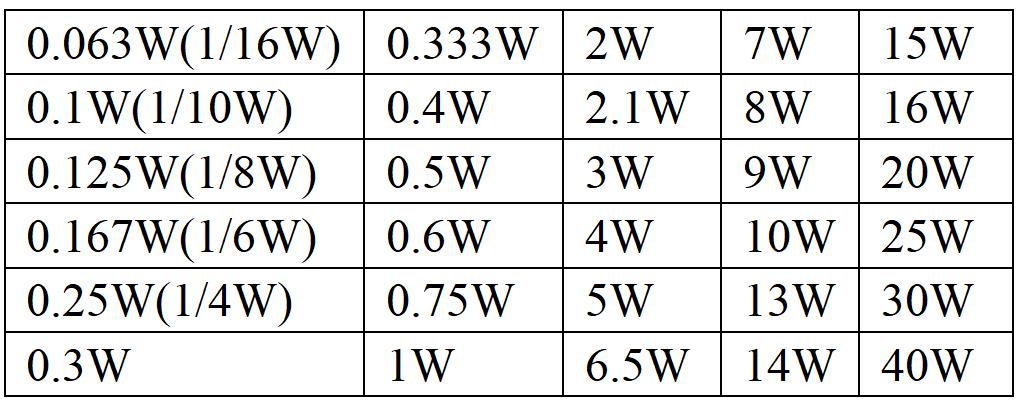
Specifies the maximum amount of power the resistor can safely dissipate without damage. If apply more power than the rating, the circuit may overheat and fail. Power ratings for a 47 Ω typically range from 0.125W (1/8W) for small signal applications to 5W for higher-power applications such as power supplies and industrial circuits.
4. Temperature Coefficient
Refer to how much the resistance value changes with temperature. For instance, ±100 ppm/°C means the resistance will change by 0.01% for each degree Celsius change in temperature. A lower temperature coefficient (e.g., ±50 ppm/°C) offers better stability in environments with fluctuating temperatures. Resistors with low temperature coefficients prefer in sensitive circuits such as precision measurement or temperature-compensated applications.
5. Voltage Rating
Indicates the maximum voltage that can apply across the resistor without causing electrical breakdown or damage. The voltage rating for a 47 Ω typically ranges from 200V to 500V, depending on the resistor’s size and power rating. It’s necessary to ensure that the applied voltage is below the 47Ω’s maximum voltage rating to avoid overheating or potential damage.
6. Current
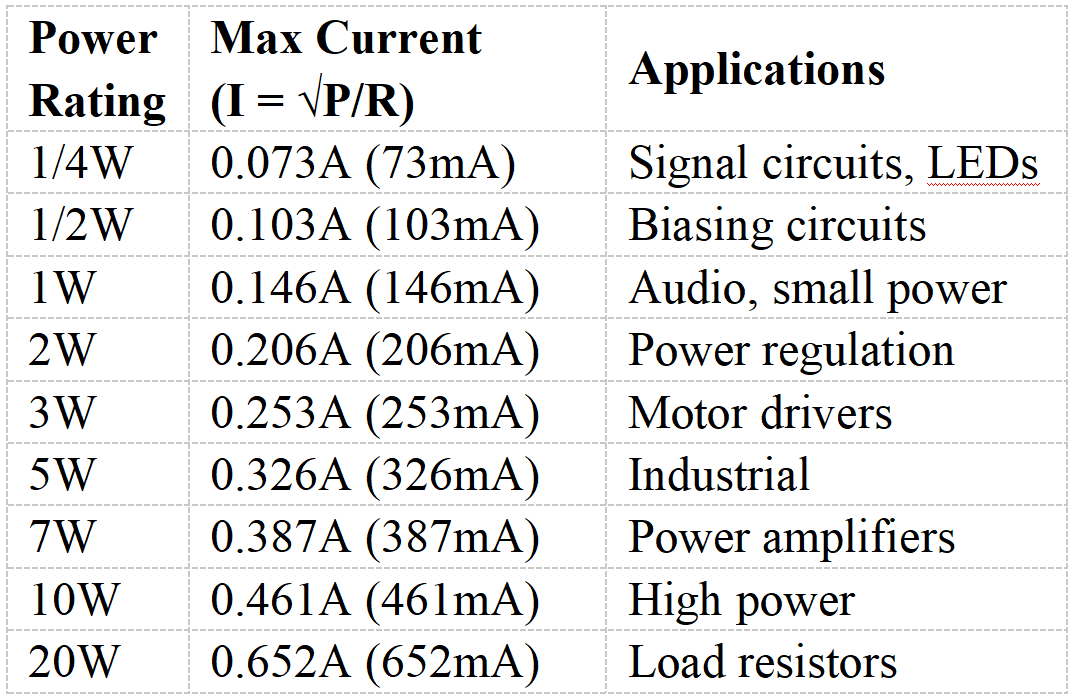
Depends on the applied voltage and the resistance value. For instance, when apply a voltage to the resistor, the current flowing through it can determine using Ohm's law. In practical terms, for a 5.6V source, a 47 Ω typically carry around 120 mA of current.
Key Specifications
Specification | Value |
Resistance Value | 47 Ω |
Tolerance | 0.05%, 0.1%,0.5% , 1%, 2% , 5% , 10%, 20% |
Power Rating | 0.125W, 0.25W, 0.5W, 1W, 2W, 5W |
Temperature Coefficient | ±100 ppm/°C to ±300 ppm/°C |
Voltage Rating | 200V to 500V |
Current (at 5.6V) | 0.12 A (120 mA) |
Power Rating vs. Maximum Current for 47 Ohm Resistors
Applications of 47 Ohms Resistor
The 47 ohms use in a wide range of applications across various industries, particularly in electronics and electrical circuits.
LED Current Limiting
One of the most common usage is for current limiting in LED circuits. LEDs require a specific amount of current to operate efficiently, and use a resistor in series with the LED to ensure that the current does not exceed the LED’s rated value, preventing damage.
Voltage Dividers
In many analog circuits, use 47-ohms in voltage divider circuits, where two resistors divide the input voltage into a desired output voltage. This is useful in signal processing, audio circuits, and measurement equipment. A 47 ohm can pair with another resistor to create a voltage divider that generates a specific reference voltage for sensors or measurement equipment.
Power Supplies and Voltage Regulation
Use in power supplies, particularly in current limiting and voltage regulation circuits. They help prevent excessive current from flowing to sensitive components and control power flow, ensuring that devices receive appropriate voltage levels.
Impedance Matching
In circuits involving audio or RF (radio frequency) signals, can use for impedance matching. Match the impedance of different components or transmission lines ensures maximum power transfer and reduces signal reflection or loss.
Signal Filtering
In filtering applications, can combine 47 ohms with capacitors to form RC filters (resistor-capacitor filters). Use these filters to smooth out voltage signals, eliminate noise, or allow certain frequency ranges to pass through. In audio equipment and radio communication circuits, use 47-ohm in filters to clean up the signal and improve performance.
Selecting the Right Resistor 47 Ohm
When select a 47 ohm resistor for your circuit, it's essential to consider a range of factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency. The following are some key considerations that should guide you in choosing the right components for your specific application.
1. Power Rating
This indicates the maximum amount of power it can safely dissipate without overheating or getting damaged.
The wattage rating is a key factor, especially for high-power circuits. If the power dissipated exceeds the resistor's rating, it can cause thermal failure, shortening the lifespan of the component.
The following are typical power rating for 47-ohm resistors:
47 Ohm 1 4 Watt Resistor: Suitable for low-power applications like signal circuits or basic voltage dividers.
47 Ohm 1/2 Watt Resistor: Commonly use in audio circuits, low-power power supplies, and voltage regulation circuits.
47 Ohm 1 Watt Resistor: Works well in general-purpose circuits where expect moderate power dissipation.
Resistor 47 Ohm 2 Watt: Ideal for slightly higher power circuits such as small power supplies and LED current limiting.
47 Ohm 3 Watt Resistor: Use in circuits where need higher power dissipation, such as in some audio amplifiers or signal processing.
47 Ohm 5 Watt Resistor: Necessary for handling higher power applications, including heavy-duty power supplies and motor control circuits.
47 Ohm 7 Watt Resistor: Found in industrial applications or power systems where require higher power.
47 Ohm 10 Watt Resistor: Suitable for large industrial circuits or systems with high current and power requirements.
Resistor 47 Ohm 20 Watt: Use in high-power applications, including large power supplies, industrial machinery, and automotive circuits.
Choosing the correct power rating ensures that your resistor will handle the power dissipation effectively without risk of overheating.
2. Tolerance
Indicates the accuracy of a resistor's resistance value compared to its nominal value. It express as a percentage, and it defines the allowable deviation from the specified resistance.
±1% tolerance: Common for most general-purpose resistors. It means that the actual resistance could vary by 1% from the nominal value of 47 ohms.
±5% tolerance: Often found in lower-cost resistors. This range is acceptable for non-critical applications where precision is not as important.
±0.5% and lower tolerances: Use for precision applications where the resistor's value needs to be close to the nominal value. These are ideal for sensitive circuits, precision measurement, and high-performance equipment.
For example, in a 47 ohm resistor with a ±1% tolerance, the actual value range from 46.53 to 47.47 ohms.
Choosing the right tolerance ensures that your circuit operates as expected, especially when require precision.
3. Temperature Coefficient
Refers to how much the resistor’s value changes with temperature. It typically give in parts per million (ppm) per degree Celsius (°C). A lower temperature coefficient means the resistor’s value remains more stable across a wide range of temperatures.
±100 ppm/°C: A standard temperature coefficient for many resistors, suitable for most general applications.
±50 ppm/°C: More precise types with better temperature stability. These are suitable for environments with significant temperature fluctuations or in precision circuits.
Low-temperature coefficient resistors (±25 ppm/°C or better): Ideal for sensitive instrumentation or high-precision circuits where the resistor's resistance must remain stable despite temperature variations.
4. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating is typically based on the power rating and the physical size of the resistor.
Voltage rating for a 47 ohm resistor varies depending on the power rating of the resistor.
For example, a 0.25W resistor have a maximum voltage rating of around 200V. 5W resistors have a higher voltage rating, around 500V or more, depending on its construction and size.
To select a 47 ohms with a voltage rating that exceeds the voltage you intend to apply in your circuit. Exceeding the voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown, component failure, or even circuit damage.
5. Other Considerations
Physical Size
The physical size of the resistor determines its ability to handle power dissipation and its suitability for various mounting methods (such as through-hole or surface-mount). Larger resistors tend to have higher power ratings and better heat dissipation.
Resistor Type (Material)
Carbon Film: Common in low-power applications with standard tolerance ratings. They are cost-effective but have higher temperature coefficients.
Metal Film: Offer better precision and lower temperature coefficients than carbon film. They are ideal for high-accuracy circuits.
Wirewound: Use in high-power applications where a resistor must handle significant heat dissipation. They often use in power supplies, amplifiers, and other high-power circuits.
Metal Oxide Film: Use for applications requiring a higher resistance range and better tolerance stability.
Frequently Asked Questions About 47 Ohm Resistor
What is 47 ohm resistor price and where to buy?
The pricing of a 47 ohm varies depending on the type, power rating, and quantity. Typically, 47-ohms are affordable, with prices ranging from $0.001 to $0.10 each for lower power versions when purchased in bulk. Higher power versions, such as 2W to 5W, cost between $0.010 to $1 per resistor. You can purchase it from suppliers such as Orwintech Electronics. Online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay also offer a wide selection at competitive prices.
Why are 47 ohm resistors so common?
Because their versatility in various electronic applications. They strike a balance between resistance and current-handling capacity, making them ideal for a wide range of circuits, including LED current limiting, voltage dividers, and impedance matching in audio and RF circuits. Their use extends to signal processing, power regulation, and RC circuits. The 47 ohm value is a commonly available standard that meets the needs of many electronics projects, making it a go-to resistor in both consumer electronics and industrial applications.
What color is a 47 ohm resistor?
The colour codes of a 47-ohm depends on whether it’s a 4-band or 5-band resistor. For a 4-band, the typical color is: Yellow (4), Violet (7), Black (multiplier x1), Gold (tolerance of ±5%). For a 5-band, the colors are: Yellow (4), Violet (7), Black (0), Gold (multiplier x0.1), and a tolerance band (such as Brown for ±1%). The color bands use to indicate the resistor’s value and tolerance.
What is a 47 ohm resistor used for?
A 47 ohm resistor use in a variety of applications, particularly for current limiting in LED circuits, where it ensures the current does not exceed the LED’s rated value. It also widely use in voltage dividers in signal processing and analog circuits, where it helps generate specific reference voltages. Additionally, it plays a role in impedance matching for audio systems and radio-frequency applications, as well as in power regulation circuits, RC filters, and time delay circuits, making it a versatile component in both consumer and industrial electronics.
How many ohms is a 47R resistor?
A 47 R is simply a 47 ohm resistor. The "R" designation often use in place of the decimal point to indicate a resistance value under 100 ohms. For example, a 47R is equivalent to 47 ohms. This shorthand commonly use in part numbers or component identification when referring to resistors with values below 100 ohms. So, when you see 47R, it means the resistance of 47-ohms.
What is the current through a 47 Ω resistor in a circuit?
The current through a 47R resistor depends on the voltage applied across it. For example, when apply a specific voltage, the current will flow through the resistor based on Ohm's Law. The 47 ohm controls the current in the circuit, ensuring that components receive appropriate levels of current, particularly in LED current-limiting applications. The exact current will vary depending on the voltage supplied and the resistor’s value of 47-ohms.
What is the maximum safe current through a 47 ohm, 2W resistor?
The maximum safe current through a 47 ohm, 2W resistor determine by the resistor’s power rating. In general, 2W design to handle a moderate amount of current safely without overheating. Exceeding the current limit could cause the resistor to fail. For this type of resistor, the current must keep below a safe threshold to ensure it does not exceed the 2W power ratings. It is important to select a 47 ohms resistors with an adequate power rating based on the expected current in the circuit.
Can a 47 ohm resistor be used for LED current limiting?
Yes, commonly use a 47-ohm for LED current limiting. LEDs require a specific current to operate, and using 47 ohms in series with the LED helps limit the current to a safe level. The exact current will depend on the voltage supplied, but a 47 ohm resistors typically works well in low-to-moderate current applications, ensuring that the LED operates within its specified current range. It prevents excessive current that could damage the LED, making it a standard choice for LED circuits.
Are 47 ohm resistors typically surface mount or through-hole?
Can find in both surface-mount (SMD) and through-hole configurations. Often use SMD resistors in modern electronic devices where space is limited and components mount directly onto the surface of the PCB. These are smaller and ideal for compact designs. Through-hole packages typically use in more robust or traditional circuit boards, such as those found in industrial applications or hobbyist projects, where the components insert into holes in the PCB and solder on the opposite side. Both types are commonly available in 47 ohm resistance.
Conclusion
The 47 ohm resistor is a staple in electronics as its versatility, availability, and wide range of package styles and power ratings. Whether you need a through-hole axial type, a precision metal film, a high-power wirewound, or a compact SMD version, there’s a 47 Ω resistor that fits the job.
From LED current limiting to impedance matching and circuit protection, the 47 Ω proves to be indispensable. Its balance of resistance value, tolerance availability, and power handling makes it one of the most commonly use resistors in electronic design worldwide.
Read More:
1. Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog