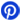
In the world of modern electronics, SMD capacitor (Surface-Mount Device) plays a key role in ensuring stable power delivery, filtering signals, and improving the performance of various devices. Unlike traditional through-hole components, SMD types design for compact and efficient assembly on circuit boards, making them essential for high-density and high-performance electronic applications. Whether you’re designing smartphones, power supplies, or automotive systems, understanding SMD capacitor is key to building reliable and efficient devices.
This guide explores everything you need to know about SMD capacitors, including the different types, how to identify them, their applications, and how to select and replace them. Let's dive into the world of Surface-Mount Device capacitors and unlock the details behind these small but powerful components.
3. SMD Capacitor Identification: Markings and Code
4. SMD Capacitor Sizes, Dimensions and Footprint
5. SMD Capacitors Applications
7. SMD Capacitor Replacement Guide
8. SMD Capacitor vs. SMT Capacitor: What’s the Difference?
9. SMD Capacitor Manufacturers
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Capacitor SMD
What is an SMD capacitor?
A type of capacitor designed specifically for surface-mount technology (SMT), where components directly mount onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) without the need for through-holes. Unlike traditional capacitors that insert into holes drilled in the PCB, SMD capacitors are compact and have leads that solder directly onto the PCB's surface. This mounting method allows for faster assembly, higher component density, and more reliable electrical connections, making them ideal for modern electronics.
SMD capacitors come in a variety of materials and types, such as ceramic, tantalum, and electrolytic, each offering distinct electrical characteristics suited for different applications. For instance, ceramic SMD capacitors (MLCC) commonly use in low-voltage, high-frequency applications, while electrolytic capacitors often employ in power supplies because their higher capacitance and energy storage capabilities.
These capacitors play a key role in electronic devices, performing functions such as decoupling (reducing noise), signal filtering, power conditioning, and energy storage. The small size and high reliability of SMD capacitors make them a crucial component in smartphones, computers, automotive systems, medical devices, and more, where space is limited, and performance is paramount.
SMD Capacitor Types
Come in various types, each with distinct materials, properties, and applications. Here’s a breakdown of common types of surface mount capacitors:
Material / Type | Properties | Common Applications |
SMD Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC) | Non-polarized, low ESR, stable performance, available in small sizes. | Decoupling, filtering, timing circuits, smartphones, laptops, RF circuits. |
SMD Electrolytic Capacitor | Polarized, high capacitance, higher leakage, larger size than MLCC. | Power supply filtering, DC output smoothing, audio circuits, voltage stabilization. |
Tantalum Capacitor SMD | Polarized, high capacitance per volume, stable, reliable, low ESR. | Mobile phones, medical devices, low-voltage circuits, precision electronics. |
Aluminium Capacitor SMD | Polarized, high capacitance, good ripple handling, larger footprint. | Power converters, LED drivers, motor control, industrial power applications. |
Capacitor Array SMD | Multiple capacitors in one package, high density, space-saving. | High-speed digital circuits, noise suppression, compact PCBs, consumer electronics. |
Film Capacitors (SMD) | Non-polarized, excellent stability, low ESR, high insulation resistance. | Audio circuits, power electronics, AC filtering, precision analog applications. |
SMD Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC)
.png)
SMD ceramic capacitors, also known as MLCCs, the most widely use types in surface-mount technology. They use ceramic as the dielectric material, offering low ESR, excellent high-frequency performance, and compact sizes. MLCCs are non-polarized and ideal for decoupling, filtering, and RF applications in smartphones, computers, and communication devices.
SMD Electrolytic Capacitor
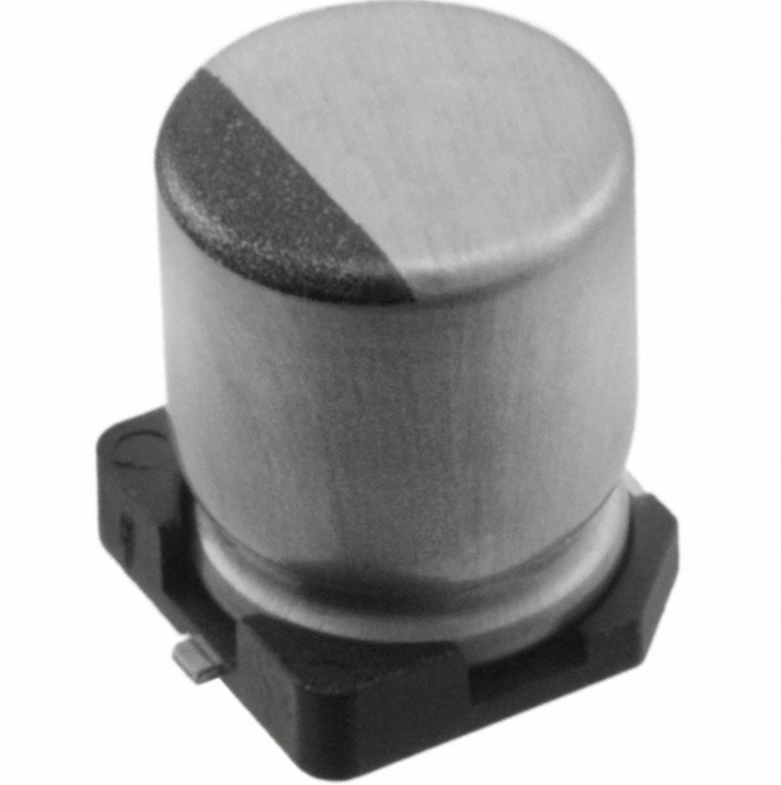

SMD electrolytic capacitors use electrolyte-based construction to achieve high capacitance values in a small package. These capacitors polarize and provide stable performance for low-frequency and power applications. They handle higher ripple currents than MLCCs and commonly use in DC power supplies, audio circuits, and voltage smoothing.
Aluminium Capacitor SMD
Use aluminum oxide as the dielectric and offer high capacitance with good ripple handling capability. They are polarized and available in larger sizes compared to tantalum or ceramic types. These capacitors commonly use in power converters, LED drivers, motor control systems, and high-current industrial circuits.
Tantalum Capacitor SMD
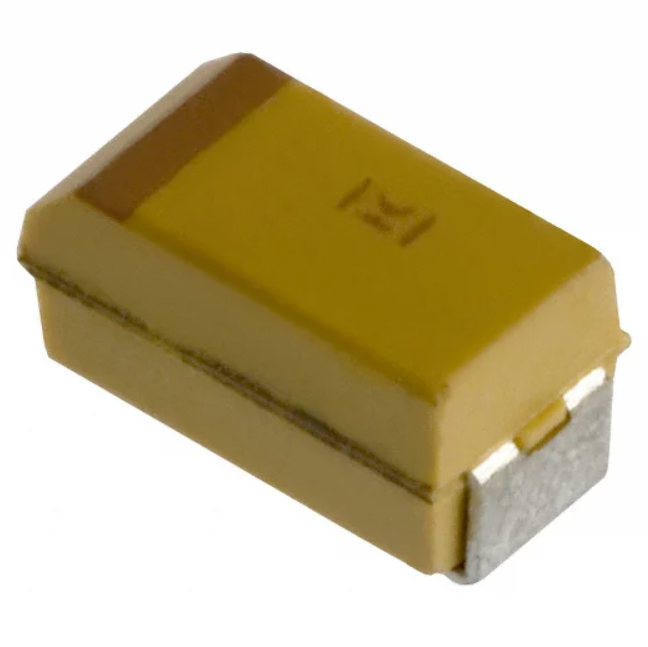

This type uses tantalum metal as the anode, producing high capacitance per volume, excellent stability, and low ESR. They polarize and perform reliably under temperature variation. Tantalum capacitors often use in mobile devices, medical electronics, and low-voltage precision circuits where need stability and compactness.
Capacitor Array SMD
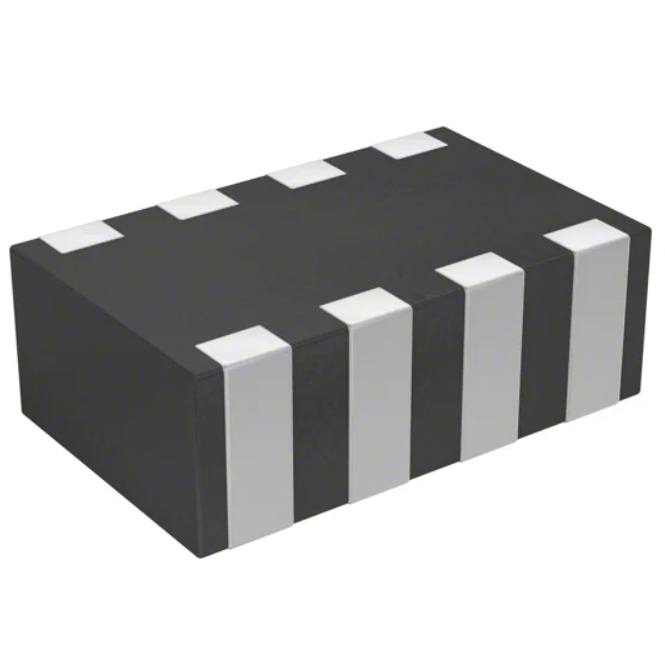

A capacitor array combines multiple capacitors in a single compact package, reducing PCB footprint and improving assembly efficiency. These arrays commonly use in high-speed digital circuits, memory modules, noise suppression networks, and compact consumer electronic boards where require many identical capacitors in a small space.
Film Capacitors (SMD)

SMD film capacitors use thin plastic films such as polyester or polypropylene as the dielectric. They offer excellent stability, low ESR, wide temperature tolerance, and high insulation resistance. These types are ideal for precision analog circuits, audio filtering, timing applications, and AC signal handling in power electronics.
SMD Capacitor Identification: Markings and Code
Unlike resistors, most SMD ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) are too small to carry visible markings. However, larger SMD capacitors—such as electrolytic, tantalum, and film types—use different marking systems to indicate capacitance, voltage, tolerance, and polarity. Understanding these codes helps identify the correct replacement and ensures proper usage in circuits.
Marking Types
SMD capacitors typically use one of the following marking systems:
1. Three-Digit Code (e.g., “103”)
This is the most common marking on larger MLCCs and film capacitors.
The first two digits represent significant figures.
The third digit is the multiplier (number of zeros in picofarads).
Example: 103 → 10 × 10³ pF → 10,000 pF → 10 nF
2. Letter-Number Code (e.g., “A104”)
Common on tantalum capacitors and some film types. The letter indicates tolerance or series code (e.g., A, B, C). The numbers indicate capacitance in pF. Example: A104 → 100,000 pF → 0.1 µF, tolerance “A”
3. EIA Standard Code (e.g., “B104K”)
Used on electrolytic, tantalum, and some polymer capacitors.
First letter: Voltage or series code
Numbers: Capacitance value (pF)
Last letter: Tolerance rating
Example: B104K → 100,000 pF → 0.1 µF, tolerance ±10%
4. Polarity Markings (for electrolytic and tantalum SMD capacitors)
Tantalum capacitors: The positive (+) terminal mark with a stripe or bar.
SMD aluminum electrolytics: The negative (–) terminal mark with a band or shaded area.
Ceramic MLCCs: Non-polarized, no polarity markings.
5. Large SMD Electrolytic Markings
Electrolytic SMD capacitors often include:
Capacitance (e.g., 47 = 47 µF)
Voltage (e.g., 6V, 10V)
Series code (manufacturer-specific)
Marking Type | Code e.g. | Description |
Three-Digit Code | 103 | The first two digits represent significant digits, and the third digit is the multiplier. For example, 103 represents 10,000 pF (10nF). |
Letter-Number Code | A104 | The first letter represents the tolerance, and the number is the capacitance value in picofarads (pF). For example, A104 represents a 100nF capacitor with ±20% tolerance. |
EIA Standard Code | B104K | The first letter represents the tolerance, and the number is the capacitance value (e.g., B104K means 100nF with ±10% tolerance). |
SMD Capacitor Sizes, Dimensions and Footprint
SMD package capacitors come in a range of standard sizes, designated by EIA (Electronic Industries Alliance) codes. Common sizes include:
EIA Size Code | Dimensions (L×W) | Typical Applications |
0201 | 0.6×0.3mm | Ultra-compact devices, smartphones, wearables, RF modules, high-density PCBs. |
0402 | 1.0×0.5mm | Mobile phones, IoT devices, compact consumer electronics, decoupling and high-frequency circuits. |
0603 | 1.6×0.8mm | General-purpose decoupling, signal filtering, automotive electronics, industrial PCBs. |
0805 | 2.0×1.25mm | Power line filtering, DC-DC converters, LED drivers, communication equipment. |
1206 | 3.2×1.6mm | Power circuits, bulk capacitance, energy storage, high-voltage applications. |
1210 | 3.2×2.5mm | High-capacitance MLCCs, power supplies, telecom equipment, industrial power modules. |
1812 | 4.5×3.2mm | High voltage, surge protection, large capacitance circuits, automotive safety electronics. |
2220 | 5.7×5.0mm | High-energy storage, capacitor banks, power distribution systems, aerospace and military electronics. |
0402 SMD Capacitor
The 0402 (1.0 × 0.5 mm) size is extremely compact and widely used in smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, and high-density PCBs. Its small size makes it ideal for RF circuits, decoupling near IC pins, and applications requiring minimal parasitics. It is one of the most common sizes in modern compact electronics.
0603 SMD Capacitor
The 0603 (1.6 × 0.8 mm) package is a general-purpose size used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, communication modules, and industrial equipment. It offers a balance of compact size and good capacitance range, making it suitable for decoupling, filtering, signal stability, and digital power rail smoothing.
0805 SMD Capacitor
The 0805 (2.0 × 1.25 mm) size supports higher capacitance values and better power handling compared to 0402 and 0603 types. It use in power supplies, DC-DC converters, LED drivers, and communication equipment. Its slightly larger size provides improved stability and high-frequency performance for many applications.
1206 SMD Capacitor
The 1206 (3.2 × 1.6 mm) capacitor design for higher voltage ratings and larger capacitance. It use in battery-powered systems, energy-storage circuits, filtering of power rails, and high-voltage electronics. Its size allows it to deliver strong performance in industrial and automotive applications.
1210 SMD Capacitor
The 1210 (3.2 × 2.5 mm) size provides significant capacitance, excellent ripple current handling, and reliable thermal stability. It commonly use in telecom systems, power modules, motor drivers, and industrial control electronics. This size favor when require high energy storage within a compact footprint.
Standard Capacitor SMD Footprint Dimensions (IPC-7351)
EIA Size Code | Typical Pad Length (mm) | Typical Pad Width (mm) | Pad-to-Pad Gap (mm) | Notes |
0402 | 0.5–0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4–0.5 | For ultra-small, high-density boards. |
0603 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | Helps prevent tombstoning. |
0805 | 1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | Most common for general electronics. |
1206 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1 | Used in power and high-voltage circuits. |
1210 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1 | For high-capacitance and high-current applications. |
Exact pad sizes vary slightly by manufacturer, but these values follow IPC-7351B (Nominal Land Pattern).
SMD Capacitors Applications
Decoupling and Bypass Capacitors
One of the primary application is in decoupling and bypass circuits. These capacitors help filter out unwanted noise and voltage spikes on power lines, ensuring stable voltage delivery to sensitive components such as microcontrollers, processors, and logic ICs. Typically, MLCCs (Ceramic Capacitors) use in these applications because their high-frequency response and low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance).
Filtering Capacitors
Widely use in filtering applications to remove high-frequency noise from power supplies, signals, and audio systems. Ceramic MLCCs and electrolytic capacitors are common in power supply filters to smooth out AC ripple or unwanted signal variations. They also use in RF circuits to filter out specific frequencies.
Energy Storage and Power Supply
In power management circuits, use to store energy and stabilize voltage levels. Electrolytic capacitors and tantalum-capacitors frequently use in DC-DC converters, voltage regulators, and power supply circuits to smooth voltage fluctuations, store energy, and ensure stable operation under varying loads.
Coupling and Signal Transfer
Use capacitors to couple or transfer signals between stages in amplifiers, communication circuits, and audio systems. SMD capacitors can block DC voltage while allowing AC signals to pass through. Ceramic MLCCs are particularly popular in audio and RF signal coupling applications because their low distortion and high-frequency performance.
Timing and Oscillator Circuits
The capacitors, in combination with resistors or crystals, play a key role in generating specific time delays or oscillation frequencies. These capacitors are integral in timing circuits and oscillators, including those found in microcontrollers, clock circuits, communications equipment, and signal generators. The frequency stability of the oscillator depends on the capacitor’s precision and quality.
RF and Microwave Circuits
High-frequency RF circuits and microwave applications often require specialized capacitors with low ESR and high Q-factor. Ceramic and film capacitors commonly use for impedance matching, tuning, and filtering in RF communication systems, antenna designs, and microwave equipment.
Automotive Electronics
Commonly use in automotive ECUs (Electronic Control Units) and other electronic systems for voltage stabilization, signal filtering, and noise suppression. Automotive capacitors design to withstand harsh conditions, including high temperatures, vibrations, and long operational lifespans. Electrolytic capacitors typically use for energy storage and filtering power rails in automotive applications.
Industrial and Medical Electronics
In industrial and medical devices, use to maintain signal integrity, power stability, and noise reduction. Capacitors in medical equipment (such as ECGs and pacemakers) ensure reliable operation and accurate measurements, while in industrial systems, they help filter power supplies and protect sensitive circuits from electrical noise.
How to Test SMD Capacitors
Testing SMD capacitors is essential to verify their functionality, detect faults, and ensure reliable circuit operation. Because of their small size and surface-mount design, testing requires careful handling and sometimes specialized tools. There are several ways to test it, depending on their type and the equipment available.
1. Visual Inspection
Before using any instruments, inspect the capacitor carefully:
Look for cracks, chips, or discoloration on the body.
Check for leakage or bulging in electrolytic or tantalum capacitors.
Ensure the pads and solder joints are intact and not corroded.
Visual inspection can often detect obvious physical damage, which is a common cause of failure.
2. Using a Multimeter
A standard digital multimeter can measure capacitance and detect shorts:
Set the multimeter to capacitance mode.
Place the probes on the capacitor terminals (polarity matters for electrolytic/tantalum types).
Compare the reading to the capacitor’s rated value. A significant deviation indicates a faulty component.
For resistance mode, a healthy capacitor will initially show a low resistance that gradually increases as it charges.
3. Using an LCR Meter
An LCR meter is more precise and can measure:
· Capacitance (C)
· Inductance (L)
· Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
· Dissipation factor (DF)
This method is particularly useful for small MLCCs or high-frequency capacitors where standard multimeters are inaccurate.
4. In-Circuit Testing
Some capacitors can test without removal:
Use a capacitance meter with in-circuit testing capability.
Ensure surrounding components (like resistors or diodes) do not interfere with the measurement.
5. Reflow or Replacement Testing
For critical applications, sometimes the capacitor remove from the board to test accurately. After testing, replace faulty capacitors and perform a functional check of the circuit.
Tips for Testing SMD Capacitors
Use tweezers or small probes for 0402–0603 size capacitors.
Always discharge the capacitor before testing to prevent damage to the meter.
Handle with care to avoid mechanical stress or bending the PCB pads.
SMD Capacitor Replacement Guide
Replacing an SMD circuit requires precision, proper tools, and careful handling as the small size of these components. Following the correct procedure ensures a reliable replacement without damaging the PCB or surrounding components.
First, identify the faulty capacitor by inspecting the PCB for burn marks, cracks, bulging, or leakage. Use a multimeter or LCR meter to measure capacitance and ESR, confirming the component is outside its rated value before proceeding.
Next, gather the necessary tools: a fine-tipped soldering iron (15–30W for small SMDs), solder wick or desoldering pump, tweezers for handling tiny components, flux for better solder flow, and a replacement SMD capacitor with identical capacitance, voltage, and tolerance.
To remove the faulty component, apply a small amount of flux on the solder joints and heat each joint with the soldering iron until the solder melts. Gently lift the capacitor off the PCB using tweezers. Use solder wick if necessary to remove excess solder from the pads.
Prepare the PCB pads by cleaning them with isopropyl alcohol to remove flux residues, ensuring they are flat and free from solder bridges or oxidation.
Place the new component in position using tweezers, making sure the polarity is correct for polarized types such as electrolytic or tantalum capacitors. Apply a small amount of flux and heat each pad briefly to solder the capacitor in place, taking care not to overheat the component or the PCB.
After soldering, inspect the joints under magnification to verify proper wetting and alignment. Use a multimeter or LCR meter to confirm capacitance and connectivity, then power on the circuit to ensure normal operation.
Always work on an ESD-safe surface when handling sensitive SMD capacitors. For small capacitors like 0201 or 0402, a hot air rework station provides better control. Avoid excessive mechanical force when placing or removing the capacitor to maintain long-term reliability and prevent damage to high-density PCBs.
SMD Capacitor vs. SMT Capacitor: What’s the Difference?
Feature | SMD Capacitor | SMT Capacitor |
Definition | Refers specifically to capacitors used in surface-mount technology (SMT). | Refers generally to any component designed for surface-mount technology. |
Scope | Narrower: only capacitors. | Broader: includes all surface-mount components like resistors and inductors. |
Relationship | SMD capacitors are a subset of SMT components. | SMD capacitors are a type of SMT component. |
Examples | MLCC, Electrolytic, Tantalum SMD capacitors. | SMT components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc. |
SMD and SMT capacitors are terms often used interchangeably, but they describe slightly different aspects of electronic components. An SMD (Surface-Mount Device) capacitor specifically refers to a capacitor designed for mounting directly on the surface of a PCB. These capacitors are compact, reliable, and available in a wide range of materials such as ceramic, tantalum, aluminum, and film. The primary purpose of an SMD capacitor is to perform the typical functions of a capacitor—decoupling, filtering, energy storage, and signal coupling—while fitting the constraints of modern high-density PCB layouts.
On the other hand, SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) type is a broader term that refers to any capacitor designed for surface-mount assembly, including all SMD capacitors. SMT is the manufacturing method, while SMD is the component type. In other words, all SMD capacitors are SMT components, but the term SMT encompasses more than just capacitors; it includes resistors, inductors, diodes, and ICs as well.
The scope of SMD capacitors limit to capacitive components, whereas SMT refers to the surface-mount manufacturing process used for various types of components. Their relationship is therefore hierarchical: SMD capacitors are a subset of SMT components specifically designed for surface mounting.
Examples of SMD capacitors include 0402 ceramic MLCCs, 1206 tantalum capacitors, and 1210 aluminum electrolytic capacitors. SMT components, meanwhile, include SMD resistors, diodes, and inductors in addition to SMD capacitors. Understanding this distinction helps designers communicate clearly when specifying components for high-density PCBs and automated assembly.
SMD Capacitor Manufacturers
Several top manufacturers provide high-quality circuits use in a wide range of applications. Below are some of the most recognized brands:
1. MURATA
Murata is a leader in ceramic SMD capacitors, especially MLCCs, used in smartphones, laptops, and automotive systems. Known for compact, high-frequency performance.
2. ROHM
ROHM offers a variety of capacitors, including ceramic, aluminum, and tantalum types. Their products are known for low ESR and reliability in power electronics.
3. SAMSUNG
Samsung manufactures MLCCs and electrolytic capacitors for mobile, industrial, and consumer electronics, focusing on compact designs and long lifespan.
4. VISHAY
Vishay provides ceramic and electrolytic SMD capacitors with high capacitance and stability, used in automotive, industrial, and telecom applications.
5. YAGEO
Yageo specializes in MLCCs, offering high-quality, reliable capacitors for consumer electronics, automotive, and telecom industries.
6. TDK
TDK produces MLCCs, tantalum, and electrolytic capacitors known for low ESR and excellent performance in power conversion, telecommunications, and automotive sectors.
7. TAIYO YUDEN
Taiyo Yuden recognize for its high-performance MLCCs, widely used in mobile devices, medical equipment, and IoT products.
8. WURTH
Wurth offers a variety of SMD capacitors, including ceramic and tantalum, used in automotive, industrial, and power supply applications, known for their durability.
These manufacturers provide high-quality components that meet the demands of modern electronics, ensuring reliability and optimal performance across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions About Capacitor SMD
How many types of SMD capacitors are there?
There are several types of this component, including ceramic (MLCC), electrolytic, tantalum, aluminum, film, and capacitor arrays. Each type varies in characteristics like capacitance, voltage ratings, and size, making them suitable for different applications, such as signal filtering, power smoothing, and energy storage in electronics.
How to identify SMD capacitor value?
Typically identified using a three-digit code (e.g., 104 for 100nF) or a letter-number code (e.g., A104). For ceramic capacitors, the first two digits represent the value, and the third is the multiplier. Always check the capacitor's datasheet or manufacturer markings for exact values and voltage ratings.
What is the most common SMD capacitor?
The most common SMD capacitors are ceramic MLCCs (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors). These widely use in applications such as decoupling, filtering, and energy storage in electronic circuits. Their popularity is because their compact size, low cost, high capacitance, and reliable performance across various voltage ratings and sizes (e.g., 0805, 0603).
What is the difference between SMD and SMT capacitors?
SMD capacitors (Surface-Mount Device) refer to capacitors specifically designed for surface mounting on PCBs, while SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) is the broader assembly method used for placing SMD components. All SMD capacitors are part of SMT, but SMT also includes resistors, inductors, and other components used in the surface-mount assembly process.
What distinguishes an SMD capacitor from an electrolytic capacitor?
SMD packages are generally small, surface-mount devices, while electrolytic capacitors are typically larger and polarized. Electrolytic capacitors often use for high capacitance and voltage ratings, while SMD capacitors (like MLCCs) prefer for low capacitance, high-frequency applications, and space-constrained designs, and are usually non-polarized.
How do I differentiate an SMD capacitor from an SMD resistor?
An SMD capacitor typically has a numerical code for capacitance (e.g., 104 for 100nF), while an SMD resistor uses a similar code but reflects resistance (e.g., 100 for 100Ω). Capacitors often appear with ceramic or tantalum bodies, while resistors usually have a uniform surface or color bands.
Do SMD capacitors have polarity, and how can I identify it?
Some component types polarize, such as tantalum and electrolytic capacitors, meaning they must connect in a specific direction. Polarity usually mark with a negative (-) sign or a band on the negative side. Non-polarized capacitors, like ceramic MLCCs, can connect in either direction.
Where can I find a comprehensive SMD capacitor code chart or datasheet?
A comprehensive SMD capacitor code chart or datasheet can find on the manufacturer’s website, such as Murata, Vishay, or Yageo. Online component distributors like Orwintech Electronics also provide datasheets with detailed information on code charts, capacitance values, tolerances, and voltage ratings for various component types.
Conclusion
SMD capacitors are essential components in modern electronics, offering reliability, compactness, and high performance across a range of applications. From ceramic MLCCs to electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, understanding the different types, values, and applications ensures effective component selection. Whether you're designing consumer electronics, automotive systems, or power supplies, knowing how to identify, test, and replace SMD capacitors will help maintain optimal circuit functionality. With leading manufacturers like Murata, Vishay, and Samsung, high-quality SMD capacitors are readily available for all your electronic design needs.
Read More:
1. The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13
What is 100 Ohm Resistor And Color Code?

100 ohm resistor color code
2025-05-17








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog