4.7K ohm resistor, also known as 4K7, is a common component in electronics, use in various circuits to limit current, divide voltage, or serve as a pull-up/pull-down resistor. Has a resistance value of 4,700 ohms (4.7K-ohms), making it a standard choice in a wide range of applications. But what exactly does a 4.7 K do, and how does it fit into your projects? Let’s dive into everything you need to know about this component.
1. What is a 4.7K Ohm Resistor?
2. Different Types of 4.7K Ohm Resistors
4. Resistance Tolerance of 4.7K Resistor
5. Power Ratings of 4K7 Resistor
6. Common Applications for 4K7 Ohm Resistor
7. 4.7K Adjustable Resistor (4K7 Variable Resistor)
What is a 4.7K Ohm Resistor?
4.7K ohm resistor is a passive electronic component use to limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. The "4.7 K" value refers to its resistance, which is 4,700 ohms. The unit "K" stands for kilo, meaning it has a resistance value of 4.7 * 1,000 ohms. Commonly use in both analog and digital circuits for a variety of functions, such as voltage dividers, current limiting, and signal processing.
The 4.7 K ohm are useful for controlling the amount of current that passes through sensitive components such as LEDs, transistors, and integrated circuits. By adjusting the resistance in a circuit, they help protect these components from excessive current that can lead to overheating or damage. The 4.7 K ohms often use in pull-up or pull-down resistor applications, particularly in digital circuits, to ensure stable voltage levels and avoid floating states that could cause erratic behavior. 4K7 resistor is equal to 4.7K-ohms. The "K" represents a factor of 1,000. Both terms are interchangeable.
Different Types of 4.7K Ohm Resistors
Several types of 4.7 K Ω available, each suited to different uses based on their construction and form factor.
Carbon Film
Made by depositing a thin layer of carbon on an insulating substrate. The resistance value control by the thickness and length of the film. This type is cost-effective and widely used in low-power applications. They generally have tolerances 5% and produce higher noise compared to metal film types. Suitable for general-purpose electronics, such as signal processing and low-frequency circuits.
Metal Film Resistor
Made by depositing a thin layer of metal onto a ceramic substrate. The resistance adjust by the metal’s composition and thickness. This types are more precise and stable than carbon film, with tolerances as low as 1% or even 0.1%. They also exhibit excellent temperature stability, making them ideal for precision applications. Metal film have low noise characteristics, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio or sensitive electronic circuits.
4K7 Chip Resistor 4.7K SMD (Surface Mount Device)

Design for surface mounting, use in modern printed circuit boards (PCBs) where solder components directly to the surface. These types are smaller and more compact than through-hole packages, making them ideal for high-density PCBs or when space is limited. SMD 4.7K commonly make from metal film for better precision and tolerance. They are available in different sizes such as 0201, 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206, 2512 etc. SMD typically use in consumer electronics, mobile devices, and compact circuits. Both 472 and 4701 are SMD code that represent a 4.7K resistor, though they follow slightly different conventions for how encode the value. The 3-digit code uses the last digit as a multiplier, while the 4-digit code separates the resistance value and multiplier more explicitly.
4.7K Resistor Arrays
Are multi-resistor packages where connect multiple resistors together in a single component for ease of placement and reduced assembly time. These arrays are useful for applications where need multiple-resistors, such as voltage division or pull-up/down networks. They are space-saving and cost-effective, commonly use in digital logic circuits, microcontroller interfacing, and signal processing systems. Arrays are available in SMD packages and typically use in modern PCB designs to reduce component count and simplify assembly.
Carbon film is inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose applications with lower precision. Metal film offers higher precision, stability, and low noise, making it ideal for sensitive circuits. SMD chip resistors are compact and use in high-density, modern electronics, mobile and wearable devices. Resistor arrays are multi-resistor packages that save space and simplify placement in PCBs, often use in logic circuits and microcontroller interfacing.
Each type serves specific applications, from low-cost, general-purpose circuits to high-precision, noise-sensitive systems, with the selection depending on size, precision, and environmental factors.
4.7K Resistor Color Code
Use the colors coding system to indicate the resistance value. For a 4.7 K Ω, the colour codes can differ based on whether it's a 4-band or 5-band.
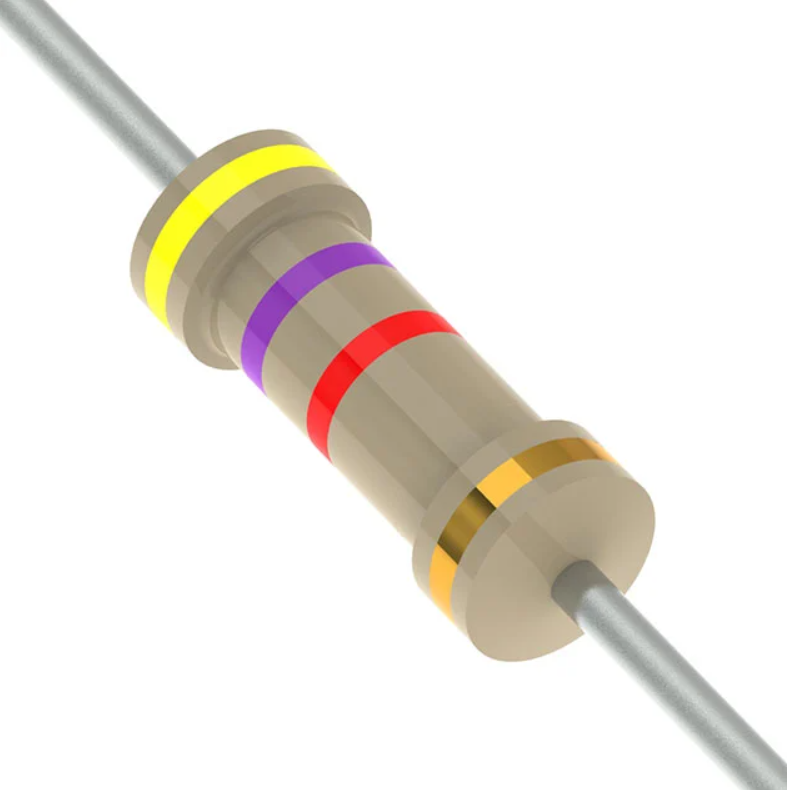
4K7 4 Band 4.7K Resistor Color
Band | Colour | Digit/Value |
1st | Yellow | 4 |
2nd | Violet | 7 |
3rd | Red | x100 Multiplier |
4th | Gold | ±5% Tolerance |
Explanation:
1st-Band (Yellow): Represents the first-digit of the value, 4.
2nd-Band (Violet): Represents the second-digit of the value, 7.
3rd-Band (Red): Multiplier of 100 (10²), so 47 * 100 = 4,700 ohms (4.7K).
4th-Band (Gold): Indicates tolerance of ±5%, meaning the actual resistance vary by up to 5% from the nominal value (4.7K).
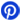
4.7K Resistor Color Code 5 Band
Band | Color | Meaning |
1st | Yellow | 4 |
2nd | Violet | 7 |
3rd | Black | 0 |
4th | Brown | x10 Multiplier |
5th | Brown | ±1% Tolerance |
Explanation:
1st-Band (Yellow): Represents the first-digit of the value, 4.
2nd-Band (Violet): Represents the second-digit of the value, 7.
3rd-Band (Black): Represents the third-digit, 0.
4th-Band (Brown): Multiplier of 10, so the value is 470 * 10 = 4,700 ohms (4K7).
5th-Band (Brown): Indicates a tolerance of ±1%, meaning the actual resistance vary by up to 1% from the nominal value (4.7K-ohms).
4 Band vs. 5 Band 4.7K Ohm Resistor
A 4-band has 2 significant digits, a multiplier, and tolerance. It offers lower precision, typically with a tolerance of ±5%, making it suitable for general-purpose circuits where high accuracy is not necessary.
A 5-band has 3 significant digits, a more precise multiplier, and typically offers a tolerance of ±1%. Use in high-precision applications where require accurate resistance values.
Key Differences:
The 5-band provides higher precision as the extra significant digit and tighter tolerance. The 4-band generally use for everyday applications, while the 5 band is ideal for circuits that require more accurate resistance values.
Resistance Tolerance of 4.7K Resistor
The tolerances indicate how much the actual resistance can deviate from the nominal value. Common tolerance values for 4.7 K ohms are:
Tolerance (%) | Resistance Range (Ohms) |
0.005% | 4,699.975 - 4,700.225 |
0.01% | 4,699.53 - 4,700.47 |
0.02% | 4,698.94 - 4,701.06 |
0.05% | 4,698.25 - 4,701.75 |
0.10% | 4,693 - 4,707 |
0.25% | 4,652.5 - 4,747.5 |
0.50% | 4,635 - 4,765 |
1% | 4,653 - 4,747 |
2% | 4,606 - 4,794 |
5% | 4,465 - 4,935 |
10% | 4,230 - 5,170 |
20% | 3,760 - 5,640 |
0.005% to 0.1%: These ultra-low tolerances use in high-accuracy circuits where precision is critical, such as in laboratory equipment or high-performance electronics. They ensure the resistance value remains close to the nominal.
0.25% to 1%: Offer good precision for most applications. 0.25% and 0.5% commonly find in precision circuits, while 1% is standard for general-purpose use in everyday electronics like consumer devices.
2% to 5%: These are standard tolerances for most commercial resistors. They’re suitable for non-critical applications where exact resistance values aren’t crucial, such as basic electronic projects or simple signal processing circuits.
10% to 20%: Often use in low-cost applications or non-precision circuits. Common in basic consumer electronics, where slight resistance variations won’t significantly affect performance.
Power Ratings of 4K7 Resistor
Indicate how much power it can safely dissipate without overheating or getting damaged. Here’s a breakdown of the different wattage ratings for a 4.7K Ω, along with their typical usages:
4.7K Ohm Resistor 1/4 Watt
0.25W is ideal for low-power applications, such as signal conditioning, voltage dividers, and basic current-limiting tasks. It commonly use in most general-purpose circuits, including microcontroller or digital logic applications.
4.7K Ohm 1/2 Watt Resistor
0.5W is suitable for moderate power dissipation requirements. Commonly use in analog circuits, sensor interfaces, or LED current-limiting applications. This rating is ideal when a bit more power is involved, such as in audio equipment or signal processing circuits.
4.7K Ohm Resistor 1 Watt
1W use in medium-power applications where higher current is flowing. It often find in amplifier circuits, voltage regulators, or audio equipment where need greater power dissipation. This rating provides better thermal stability than lower power-rated type.
Resistor 4K7 Ohm 2 Watt
2W use in circuits with higher current flow, such as motor control circuits, high-current sensor applications, or power supply circuits. 2 watts are also useful in signal processing circuits where voltage or current levels are higher.
4.7K 3 Watt Resistor
3W design for high-power circuits and commonly use in power electronics, HVAC systems, or load resistors for testing equipment. 3-watts provide greater thermal dissipation and can handle higher current or voltage applications.
4.7K 5 Watt Resistor (4K7 5W)
5-watts use in industrial applications, power supplies, high-current circuits, and high-performance audio equipment. The higher power rating allows for stable operation under heavy loads, making it suitable for electronic devices with higher energy dissipation demands.
Resistor 4K7 10W
10 watt use primarily in high-power applications such as electrical testing, industrial equipment, and high-voltage circuits. 10 watts design to withstand high temperatures and can handle significant amounts of energy without failure, making them ideal for use in power supplies, battery charging circuits, or power resistors for load testing.
Choosing the Right Power Rating
The wattage ratings determines the heat dissipation capability of the circuit. To choose the correct one to ensure the component doesn't overheat and fail in a given application. For most everyday tasks, 1/4 or 1/2 watt suffice. However, for high-current circuits, require 1-watt, 2-watt, or higher ratings to prevent overheating.
Common Applications for 4K7 Ohm Resistor
Limit Current in BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor): Often use 4.7K-resistor in the base circuit of a BJT to limit the current flowing into the base, protecting the transistor and controlling its operation.
LED 4.7K Resistor: In series with an LED, a 4.7 K limits the current, ensuring that the LED operates within its rated current, preventing damage and prolonging its lifespan.
Pull-Up Resistor: Use in digital circuits to ensure a stable "high" logic level when no active signal is driving the line, particularly in open-collector or open-drain configurations.
Voltage Divider Circuits: Use in voltage divider applications, the 4.7 K helps scale down the voltage to desired levels for components like ADC or other sensors.
Signal Conditioning: In analog circuits, a 4.7K-resistor helps with signal conditioning, filtering, and impedance matching, ensuring that signals are within acceptable levels for amplifiers or analog-to-digital converters.
Feedback Resistor in Op-Amp Circuits: In op-amp configurations, often use a 4.7K Ω in the feedback loop to set the gain of the amplifier, whether in inverting or non-inverting configurations.
RC Timing Circuits: A 4.7K, when paired with a capacitor, is commonly use in RC circuits to set time constants for oscillators, filters, or timing applications like pulse generation.
Biasing Resistor in Transistor Circuits: Use in transistor biasing, a 4K7 helps establish the proper operating point (Q-point), ensuring the transistor operates in its optimal region and remains stable.
Passive Networks for Audio Applications: In audio circuits, a 4.7K can be part of low-pass or high-pass filters, helping shape the audio signal by removing unwanted frequencies and controlling signal levels.
In digital logic circuits, can also use a 4.7K as a pull-down resistor to ensure a stable "low" logic level, preventing undefined states in input lines.
Signal Termination in Communication Lines: In communication systems like I2C, RS-232, or Ethernet, can use a 4.7K for impedance matching or signal termination, ensuring proper signal transmission and preventing interference.
4.7K Adjustable Resistor (4K7 Variable Resistor)
A 4.7K Adjustable (Variable) Resistor, often referred to as a potentiometer or rheostat (depending on its application), is a type of resistor whose resistance value can adjust manually. It allows for variable resistance, making it useful in circuits where need fine adjustments to the current or voltage.
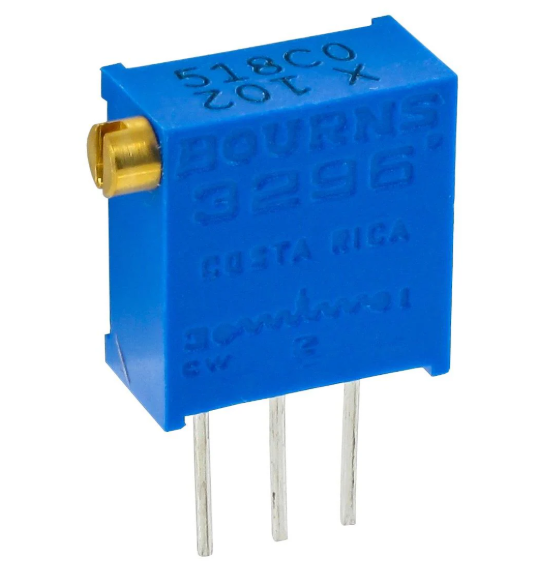
Key Features of a 4K7 Adjustable Type:
Range: The resistance can vary from 0 to 4.7K ohms, depending on the design. This adjustment allows for precise control over the resistance in a circuit.
Adjustability: Typically, have a knob or screw that allows users to change the resistance value. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as volume-control, brightness control, or tuning circuits.
Wiper: A central wiper arm moves across the resistive track, adjusting the resistance as it slides. This creates an adjustable voltage divider when connected in a circuit.
Applications of 4.7K Variable-Resistor:
Volume Controls: Use in audio circuits to adjust the volume level by controlling the current to speakers or other audio devices.
Tuning Circuits: Often use in radio receivers, oscillators, and frequency synthesizers where precise adjustments to the resistance are necessary for tuning.
Brightness Control: In lighting circuits, especially LED or dimmer circuits, to adjust the brightness by changing the resistance.
Calibration: In testing and measurement equipment, use to calibrate or fine-tune circuits to the desired specifications.
Feedback Control in Op-Amps: In op-amp circuits, can use to control the gain by varying the feedback resistance.
Types of 4.7K Adjustable Resistors:
Potentiometer: A 3-terminal device with adjustable resistance between two terminals. Often use in voltage divider circuits where the output voltage depends on the wiper's position.
Rheostat: A 2-terminal variable type use mainly for adjusting current in a circuit, such as controlling the brightness of lights or the speed of motors.
These adjustable types provide flexibility and control in a wide range of electronic applications, from simple tuning tasks to complex signal processing circuits.
FAQ about Resistor 4.7K
What does 4K7 resistor mean?
A 4K7 refers to a resistor with a value of 4.7 kilo ohms (4.7K), where K represents 1,000 Ω. The value 4.7K commonly use in various electronic circuits for applications such as current limiting, voltage division, or signal conditioning. The "K" stands for "kilo," so 4K7 is just another way of expressing 4.7K-ohms in shorthand.
What is 4.7K ohm resistor price and where to buy?
The prices of a 4.7 K Ω varies depending on factors like quantity, manufacturer, and type (e.g., carbon-film, metal film). A typical price for a single 4K7 ohm is around $0.001 - $0.01 USD. You can buy them from electronics retailers like Orwintech Electronics. Bulk purchases can reduce the per-unit cost significantly.
What color is a 4.7 K resistor?
4.7 K resistors typically follow the yellow-violet-red-gold colour code in a 4 band resistor, where:
· Yellow = 4
· Violet = 7
· Red = x100 (multiplier)
· Gold = ±5% tolerance.
In a 5-band type, it’s yellow-violet-black-brown-brown for higher precision with a ±1% tolerance.
What is the value of a 4.7 K ohm resistor?
The value of a 4.7 K is 4,700 ohms, which means it limits the current to a specific amount in a circuit, depending on the voltage. This value often use in voltage dividers, current-limiting applications, and other general-purpose circuits where need a moderate resistance. The "K" stands for kilohms, meaning 1,000 ohms, so 4.7K-ohms equals 4.7 times 1,000 Ω.
How many ohms is 4.7 k?
4.7K is shorthand for 4,700 ohm. The "K" represents kilohms, which is a unit of resistance equal to 1,000-ohms. Therefore, 4.7K resistors has a resistance value of 4,700-ohms, often use in various electronic applications to control current flow, set voltage levels, or protect components.
What is the equivalent resistance if I don't have a 4.7k Ohm resistor?
If you don't have a 4.7K, you can combine other resistors in series or parallel to achieve a similar resistance value. For instance, combining a 4.3K and a 470-ohm resistor in series would give you 4.7K ohms. Alternatively, you can combine multiple resistors in parallel to approximate the same resistance, but the specific combination depends on the available resistance values.
What is the function of a 4.7k Ohm resistor in a typical circuit?
A 4.7 KΩ often use to limit current, set voltage levels, or divide voltages in a circuit. In voltage divider circuits, it helps scale down voltages. In transistor circuits, it can limit current to the base of a transistor. It also commonly use as a pull-up or pull-down resistor in digital circuits, ensuring a stable logic level and avoiding floating states in input pins of microcontrollers or logic gates.
Can I use a 4.7k Ohm resistor as a pull-up resistor?
Yes, a 4.7 K commonly use as a pull-up resistor in digital circuits. It typically place between the input pin of a device (like a microcontroller) and the positive voltage supply to ensure the input pin reads a high logic level when no active signal is present. A 4.7K provides a good balance between power consumption and response time for most applications, such as I2C or SPI communication.
Is 4.7K the same as 4K7?
Yes, 4.7K and 4K7 refer to the same resistance value of 4,700 ohms. The term 4K7 is simply a shorthand way of writing 4.7 K (kilohms). Both expressions commonly use in electronics to represent the same resistance value, and they are interchangeable when specifying resistors. The K stands for 1,000 ohms, and the 7 represents the decimal place.
Understanding the properties and uses of a 4.7K ohm resistor is essential for anyone working with electronic circuits. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, this resistor is a reliable component that can find in various electronic devices and systems.
Read More:
1. 4.7 Ohm Resistor: A Complete Guide
2. 47 Ohm Resistor: Color Code, Specifications and Applications
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13
What is 100 Ohm Resistor And Color Code?

100 ohm resistor color code
2025-05-17








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog