The BAV99 is a high-speed switching diode that plays key role in various applications where fast response time, low capacitance, and compact packaging are critical. This diode encapsulate in a small SOT23 (TO-236AB) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package, making it ideal for modern electronics with space constraints.
In this blog post, we'll explore the BAV99 diode in detail, including its pinout, applications, key features, advantages, and some common alternatives.
2. BAV99 Pinout, Pin Configuration and CAD Model
4. BAV99 Diode Key Features and Technical Specifications
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of BAV99 Circuit
6. HDMI Circuit Protection Using BAV99 Diode
7. Differences Between BAV99 Diodes and TVS Tubes
8. BAV99 Manufacturer and Substitutes
9. Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]

What is the BAV99 Diode?
The BAV99 is a high-speed switching diode package in a small SOT23 (TO-236AB) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD). It features fast response times with a reverse recovery time (trr) of ≤ 4 ns and low capacitance (Cd ≤ 1.5 pF), making it ideal for high-speed applications such as signal processing and reverse polarity protection. The diode commonly use in compact, low-power circuits and often find in consumer electronics, communication devices, and automotive applications. It is available in dual-diode configuration, offering both convenience and efficiency in space-constrained designs..
BAV99 Equivalent Diode
BAV70 – Dual high-speed switching diode with similar structure and speed; often used in place of BAV 99.
BAW56 – Another dual switching diode with comparable reverse voltage and switching performance.
SBAV70 – High-speed dual diode optimized for low leakage and fast switching, suitable for BAV 99 replacement.
MMBD1503 – High-speed SMD diode with similar electrical behavior, often used as a direct SOT-23 substitute.
These diodes share similar characteristics and can use as substitutes depending on your specific requirements.
BAV99 Pinout, Pin Configuration and CAD Model
Understanding the pinout and configuration of the diode is necessary for correctly integrating it into a circuit. Here's a breakdown of the pinout:
Pin Configuration:
Pin 1 — Diode-1 Anode (A1): anode of the first diode.
Pin 2 — Diode-2 Cathode (K2): cathode of the second diode.
Pin 3 — Common (Cathode-1 / Anode-2, K1 / A2): cathode of diode-1 and anode of diode-2 (the shared center node).
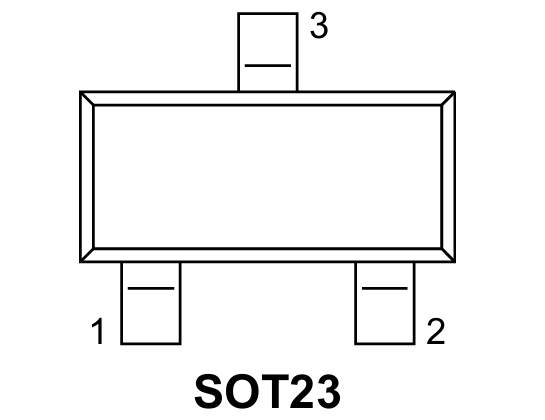
BAV99 Connection Diagram:
In the BAV 99, both diodes share a common pin, which is useful for applications where space and simplicity are key.
BAV99 Application
The BAV99’s features make it ideal for several high-speed and protection applications:
High-speed switching – The diode excels in circuits that demand extremely fast transitions, such as digital logic paths, clock distribution networks, and high-frequency communication stages. Its low junction capacitance and ≤4 ns recovery time help preserve signal integrity, making it ideal for timing-critical designs and fast pulse shaping.
Reverse polarity protection – It widely use in low-power electronics to guard microcontrollers, interface ICs, and delicate analog sensors against accidental reverse voltage. By blocking incorrect polarity at the input, the BAV 99 prevents permanent damage and ensures long-term device reliability.
General-purpose switching – Its compact SOT-23 package and dual-diode configuration make it suitable for everyday switching tasks, including signal routing, diode-OR logic, biasing networks, small-signal control, and isolation between circuit stages in consumer, industrial, and communication devices.
Level shifting between mixed-voltage circuits – The diode often use where different logic families must interface, such as 5V microcontrollers talking to 3.3V or 1.8V devices. Its predictable forward voltage and fast behavior allow it to shape and translate logic levels without distorting high-speed signals.
Signal clamping, limiting, and transient protection – Designers use the BAV 99 to keep sensitive nodes within safe voltage thresholds. Effective in limiting overshoot on analog inputs, stabilizing communication lines, suppressing small ESD spikes, and protecting ADC or comparator inputs from fast voltage transients.
Small-signal rectification in RF and high-frequency circuits – Because its low capacitance and fast switching, the BAV99 performs efficiently in RF detectors, demodulators, fast AC-to-DC converters, amplitude sensing circuits, and precision monitoring stages. It often use where slow rectifiers will distort or lag behind dynamic signals.
BAV99 Diode Key Features and Technical Specifications
Here are some of the standout characteristics and technical specifications of the diode:
High switching speed: With a reverse recovery time (trr) of ≤ 4 ns, the circuit ensures fast response times in high-speed circuits.
Low capacitance: The chip has a junction capacitance (Cd) of ≤ 1.5 pF, which reduces signal distortion and improves overall performance.
Low leakage current: The diode operates with low reverse leakage current, which is key for sensitive applications.
Reverse voltage: The diode can handle a reverse voltage (VR) of up to 100 V, providing reliable performance even in high-voltage environments.
Small SMD package: The BAV 99 comes in a small SOT23 package, making it suitable for modern compact devices.
BAV99– Technical Specifications
Here are the key technical specifications of the diode that highlight BAV99’s performance and suitability for various high-speed, low-power applications:
Parameter | Value |
Reverse Recovery Time (trr) | ≤ 4 ns |
Junction Capacitance (Cd) | ≤ 1.5 pF |
Reverse Voltage (VR) | ≤ 100 V |
Forward Voltage (Vf) | ~0.7 V (typical) |
Peak Forward Current (If) | 200 mA (max) |
Average Forward Current (If(av)) | 100 mA (max) |
Peak Power Dissipation | 200 mW (max) |
Operating Temperature Range | -65°C to +150°C |
Storage Temperature Range | -65°C to +150°C |
Package Type | SOT-23 (TO-236AB) |
Package Dimensions (SOT-23) | 2.9 x 1.6 x 1.1 mm |
Diode Configuration | 1 Pair Series Connection |
Mounting Type | Surface Mount |
Base Product Number | BAV99 |
Other Key Characteristics:
Low Leakage Current: Ensures minimal reverse leakage and greater reliability in low-power circuits.
Small Package: The SOT-23 form factor allows for integration into small, space-constrained PCB designs.
Dual Diode Configuration: Offers a compact solution for applications requiring two diodes in a single package.
These technical specs make the diode well-suited for high-speed switching, protection, and small-signal rectification in digital, analog, and RF applications.
BAV99 SOT23 Dimensions:
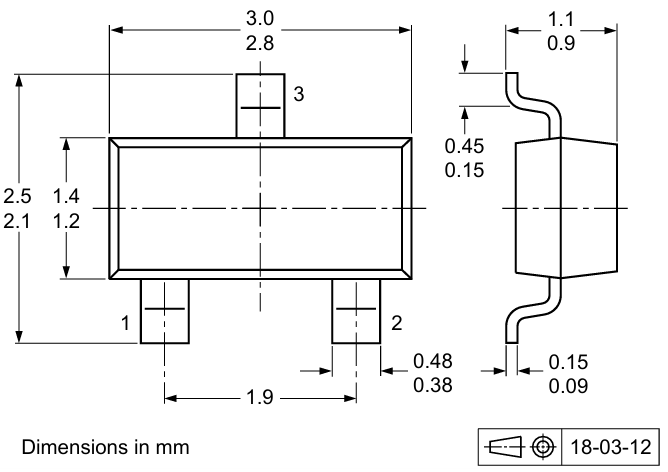
The SOT-23 package sizes for the BAV 99 are as follows:
· Length: 2.9 mm
· Width: 1.6 mm
· Height: 1.1 mm
Advantages and Disadvantages of BAV99 Circuit
Advantages of the BAV 99 Circuit
High Switching Speed
The chip has a reverse recovery time of ≤ 4 ns, making it ideal for fast switching in digital, clock, and RF circuits.
Low Capacitance
With ≤ 1.5 pF junction capacitance, it ensures clear, undistorted signals, making it suitable for high-frequency applications.
Compact Package
Its small SOT-23 package is perfect for space-limited designs, allowing easy integration into dense PCBs.
Low Leakage Current
The BAV 99 has minimal reverse leakage, improving efficiency in low-power and battery-operated devices.
Versatile Use
It works well in high-speed switching, reverse polarity protection, and signal clamping applications.
Dual Diode Configuration
Two diodes in a single package save space and cost in circuits requiring two diodes.
Disadvantages of the BAV 99 Diode
Limited Reverse Voltage (100V)
With a reverse voltage of only 100 V, it is not suitable for high-voltage circuits.
Not for Power Applications
The diodes design for low-power use and can't handle high currents or large power dissipation.
Limited Surge Protection
It doesn't handle large voltage spikes like TVS diodes, making it unsuitable for heavy transient protection.
Not Ideal for High-Voltage Protection
Its low reverse voltage rating makes it unsuitable for circuits needing high-voltage protection.
Less Efficient in High-Power Circuits
It cannot perform well in power-heavy designs as its small size and low current rating.
HDMI Circuit Protection Using BAV99 Diode
The BAV 99 diode is ideal for HDMI circuit protection as its fast switching speed and low capacitance, which are crucial for high-speed signal integrity. HDMI devices are vulnerable to reverse polarity, voltage transients, and electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can damage sensitive components. Here's how the diode can protect HDMI circuits:
Reverse Polarity Protection: By placing the BAV99 in the power path, it can block reverse voltage, protecting the HDMI components from damage because incorrect connections.
Transient Voltage Suppression: The BAV99’s fast switching response allows it to protect against small voltage spikes and transients in the HDMI signal lines, preventing damage to the transmitter and receiver.
Signal Clamping: Can use the diode to clamp voltage on HDMI data lines (like TMDS) to ensure that the signal stays within safe levels, preventing signal distortion and maintaining clarity during transmission.
ESD Protection: The diode's low leakage current and high-speed recovery time make it an effective choice for safeguarding against electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can degrade signal quality or damage circuitry.
In summary, the diode offers efficient, low-cost protection for HDMI circuits, ensuring reliability in high-speed and high-frequency environments.
Differences Between BAV99 Diodes and TVS Tubes
The BAV 99 diode and TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) tubes are both used for circuit protection but serve different roles.
Function: The BAV99 diode primarily use for high-speed switching, reverse polarity protection, and small transient suppression in low-power, high-speed circuits. It designs to protect against minor voltage spikes in applications such as data lines and HDMI. In contrast, TVS tubes design to protect against large voltage transients caused by events like lightning or electrostatic discharge (ESD), offering robust protection for high-power systems.
Response Time and Voltage Handling: The BAV99 has a fast switching time (≤4 ns) and handles low to moderate voltages (up to 100V). TVS tubes, while slower, can handle high-energy surges (hundreds of volts) and offer stronger transient protection.
Applications: The diodes suite for low-energy circuits such as signal clamping in HDMI, logic gates, and small-signal designs. TVS tubes use in high-power applications such as power supply lines and telecommunications.
Size and Durability: The diode is compact and designed for space-limited circuits, while TVS tubes are larger and built for high-energy surge protection, offering longer durability under high-power conditions.
In summary, the diode is ideal for small-signal protection, while TVS tubes are better for high-energy surge protection.
BAV99 Diode Datasheet: PDF
BAV99 Manufacturer and Substitutes
The BAV 99 diode manufacture by several prominent electronics companies, each offering the circuit with slight variations in specifications, packaging, and availability. Here are some of the key manufacturers of the diode:
Fairchild
A well-known semiconductor manufacturer, Fairchild offers the BAV 99 diode with high-speed switching and low capacitance, suitable for general-purpose and high-speed applications.
Nexperia (NXP / Philips)
Nexperia produces high-quality diodes like the BAV99, emphasizing precision and performance in signal switching and protection applications.
Infineon
Known for its innovation in power and protection diodes, Infineon offers the BAV 99 with reliable performance in both signal processing and transient protection.
ON Semiconductor
ONsemi provides the BAV99 diode in various packaging options, suitable for consumer electronics and communication circuits that require efficient switching and protection.
Vishay
Vishay manufactures the BAV 99 with a focus on high-speed signal switching and low-leakage current, offering protection for sensitive electronic components.
Panjit
Panjit is known for affordable, high-performance diodes like the BAV 99, widely use in industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.
Diodes Incorporated
A leading supplier of small-signal diodes, Diodes Inc. provides the BAV 99 as a reliable option for circuit protection, with consistent quality and availability.
Diotec
Diotec manufactures the BAV99 as part of its wide range of small-signal diodes, focusing on reliability and cost-effectiveness for consumer and industrial electronics.
These manufacturers ensure that the BAV99 diode is available in various configurations to meet the needs of different industries, from high-speed switching to general-purpose circuit protection.
BAV99 Substitutes (Different Brands):
Part Number | Manufacturer | Description |
BAV99-7-F | Diodes Incorporated | Dual high-speed switching diode, SMD package |
BAV99-13-F | Diodes Incorporated | Dual diode in SOT-23 package |
BAV99-E3-08 | Vishay | Small signal switching diode, SMD package |
BAV99-E3-18 | Vishay | Low-leakage, fast-switching dual diode |
BAV99-TP | MCC (Micro Commercial Components) | SMD dual diode, designed for fast switching and general protection |
BAV99,215 | NXP | Dual diode, part of NXP's small-signal diodes series |
BAV99,235 | NXP | Compact, low-leakage dual diode, SOT-23 package |
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
What is BAV99 price?
The pricing of a BAV 99 diode typically ranges from $0.005 to $0.050 USD per unit, depending on the supplier, quantity purchased, and packaging type. Bulk orders or purchasing through authorized distributors offer discounts. Prices vary across different regions and for different manufacturers.
What defines a switching diode?
A switching diode is a type of diodes designed for fast switching between ON and OFF states. It has a low reverse recovery time (trr), making it suitable for high-speed circuits. Switching diodes use in applications that require rapid response times, like digital logic, signal routing, and protection circuits.
What applications is the BAV99 suitable for?
The diode is suitable for high-speed switching, reverse polarity protection, signal clamping, and small-signal rectification. It commonly use in applications like HDMI circuits, data lines, logic gates, and communication ports, where fast response and low capacitance are essential for protecting components and ensuring signal integrity.
What temperature range can the BAV99 operate within?
The diode can operate in a wide temperature range, typically from -65°C to +150°C. This makes it suitable for use in both consumer electronics and industrial applications that may expose to varying environmental conditions, ensuring reliable performance even under extreme temperatures.
What is the through-hole counterpart of the BAV99?
The through-hole counterpart of the BAV99 is generally the 1N4148 or 1N914 diodes. These diodes offer similar fast-switching characteristics but come in through-hole packages instead of the compact SMD form of the BAV99. They are suitable for applications requiring a high-speed small-signal diode with a larger, more robust package.
What can the BAV99 be used for?
The diode can use for signal protection, small-signal switching, reverse polarity protection, clamping voltage in high-speed digital circuits, and ESD protection in communication systems. Its compact size and fast-switching capabilities make it ideal for low-power, space-constrained applications.
How does BAV99 work?
The BAV99 functions by allowing current to flow in the forward direction when the anode is more positive than the cathode. In reverse bias, it blocks current flow. In high-speed switching, the diode rapidly switches between ON and OFF states, protecting circuits by clamping excessive voltage or preventing reverse current from damaging sensitive components.
Conclusion
The BAV99 diode is an excellent choice for circuits requiring high-speed switching, low capacitance, and compact packaging. With its versatile applications in signal processing, reverse polarity protection, and general-purpose switching, the diode continues to be a staple component in modern electronics. Whether you're designing small, high-speed circuits or protecting devices from voltage spikes, the BAV 99 offers a reliable and efficient solution.
Read More:
1. LM317T Voltage Regulator: Pinout, Datasheet and Equivalent
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13
What is 100 Ohm Resistor And Color Code?

100 ohm resistor color code
2025-05-17








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog