The MAX232 IC is widely use RS-232 line driver/receiver designed for reliable, low-cost data transmission between microcontrollers and other serial devices that use the RS232 standard. It plays a key role in systems where communication occurs between logic-level (TTL or CMOS) devices and that require RS-232 voltage levels. In this post, we’ll dive into the features, pin configuration, variants, applications, and how it compares to other similar ICs such as MAX3232.
2. MAX232 Chip Features and Working Principle
3. MAX232 IC Pinout, Pin Configuration and Roles
4. MAX232 IC Variants and Packages, Dimensions
8. MAX232 vs. Other RS232 Interface Chip MAX3232 IC
9. Frequently Asked Questions[FAQ] about MAX232
What is the MAX232 IC?
This chip is a line driver/receiver designed for EIA/TIA-232E and V.28/V.24 serial communication standards. Primarily use to convert the voltage levels between RS-232 devices and TTL/CMOS logic systems. RS232 requires voltage levels of ±12V, which can be difficult to generate in systems that only supply +5V or +3.3V. The MAX 232 solves this issue by using an integrated charge pump to generate the necessary +12V and -12V from a single +5V supply. This makes it ideal for applications where a dual-voltage supply is unavailable.
The circuit widely use in serial communication applications, such as microcontroller interfaces, modem connections, and data transmission between computers and peripheral devices. It simplifies design and saves space by integrating both the voltage conversion and signal conditioning in a single chip.
The MAX232’s family offer in 3 different packages, making it flexible for various design needs. These packages support a wide range of temperature ratings from 0°C to +70°C up to -55°C to +125°C, allowing for use in both commercial and industrial environments. This makes it an essential component for reliable communication in systems requiring RS-232 signal conversion.
Alternative and Replacement to the MAX232 include:
RS232: Refers to the standard for serial communication, not a specific IC, but many such as the MAX 232 design to interface with it.
MC148: A line driver/receiver use in RS-232 communication, offering similar functionality to the MAX 232, but less commonly used.
FT232RL: A USB-to-RS232 converter chip, used to bridge USB and RS-232 devices, supporting more modern USB interfaces.
MAX3232: A direct replacement for the MAX 232, designed to operate at lower voltages (3V to 5.5V) while providing similar performance for RS-232 communication. Widely use in modern, low-voltage applications.
MAX232 Chip Features and Working Principle
The MAX 232 IC design to simplify RS-232 communication by offering a range of integrated features that enhance both performance and efficiency. It reduces the need for external components, saving valuable board space. The IC includes integrated charge pump circuitry, which generates the necessary ±12V required for RS-232 communication from a single +5V supply. This eliminates the need for a bipolar ±12V power supply, making it ideal for systems with limited power sources or space constraints.
Additionally, the MAX232 enables single-supply operation, which means it can function with just a +5V supply, making it more compatible with modern, low-voltage digital systems. The IC also features a 5μW shutdown mode, greatly reducing power consumption when not in use. This makes it well-suited for applications that require low power consumption, such as battery-powered devices or energy-efficient systems.
MAX232 IC Schematic
Here’s a basic overview of how the circuit works:
The chip requires external capacitors (typically 1µF) to function as charge pumps that generate the ±12V needed for RS-232 communication.
It has two line drivers and 2 receivers that convert data between RS-232 voltage levels (±12V) and TTL/CMOS logic levels (0V to 5V).
The MAX232’s simple and effective design makes it one of the most popular ICs for serial communication between TTL/CMOS systems and RS-232 devices.
MAX232 Working Principle
The IC functions as a voltage level translator for serial communication between RS-232 and TTL/CMOS logic systems. It converts TTL/CMOS logic levels (0V to 5V) to RS-232 levels (±12V) and vice versa, enabling communication between devices with different voltage requirements.
The IC uses internal charge pump circuitry to generate the ±12V needed for RS-232 communication from a single +5V supply. This achieve by using external capacitors in a voltage multiplier configuration.
When transmitting data, the MAX 232 converts TTL signals to RS-232 voltage levels, allowing for proper signal transmission to RS-232 devices. Conversely, it converts incoming RS-232 signals (±12V) into TTL logic levels for microcontrollers or other TTL devices.
The circuit power by a +5V supply and is highly efficient, including a 5μW shutdown mode to minimize power consumption when idle. This makes it ideal for low-power and battery-operated systems.
Overall, the MAX 232 provides a reliable and compact solution for converting data between TTL/CMOS and RS-232 devices.
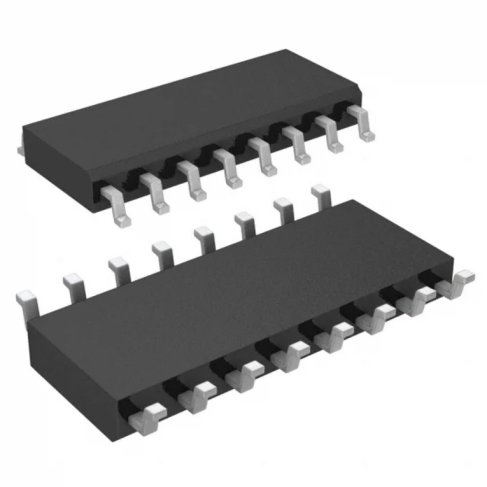
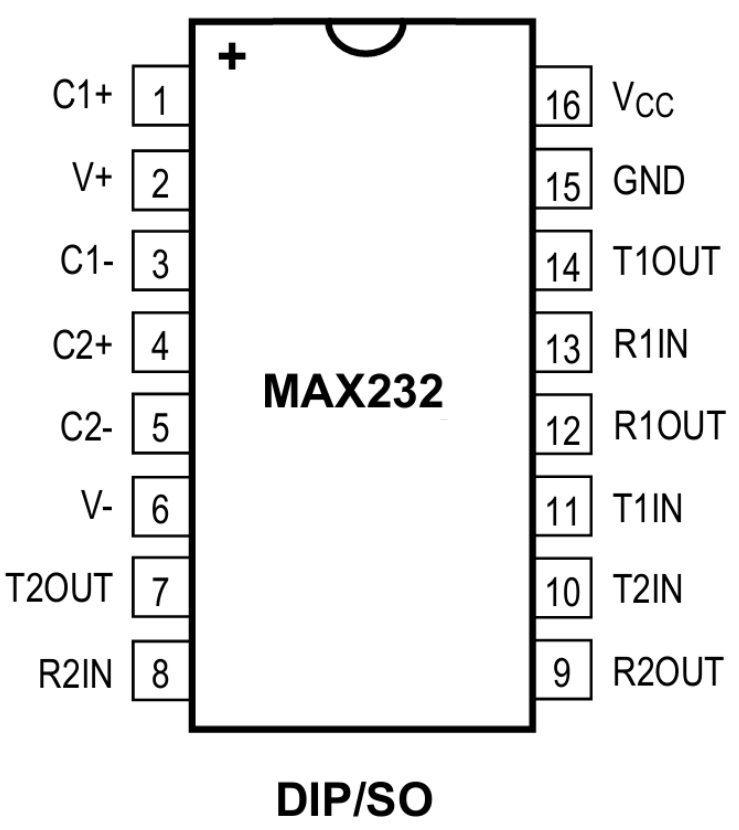
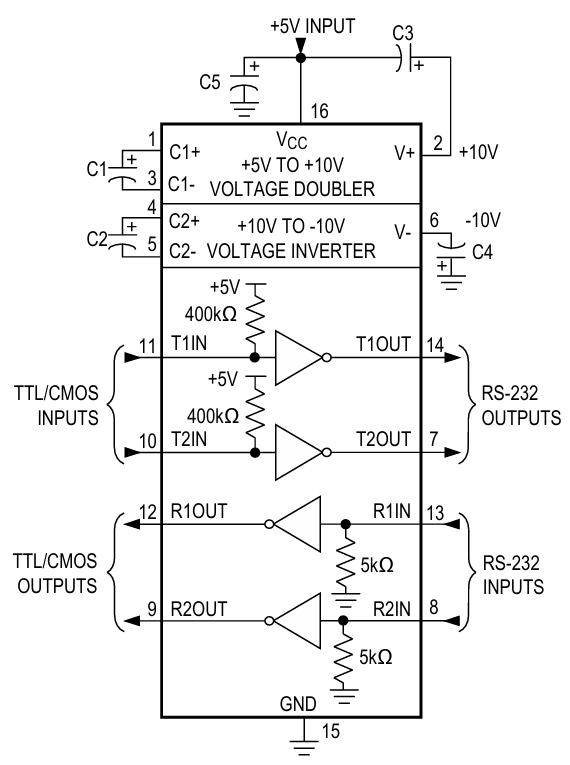
MAX232 IC Pinout, Pin Configuration and Roles
The IC comes in a 16-pin configuration. Below is a breakdown of the key pins:
Pin No. | Symbol | Pin Name |
1 | C1+ | Output of external capacitance of positive voltage multiplier unit |
2 | V+ | Output of positive voltage from multiplier unit |
3 | C1- | Output of external capacitance of positive voltage multiplier unit |
4 | C2+ | Output of external capacitance of negative voltage multiplier unit |
5 | C2- | Output of external capacitance of negative voltage multiplier unit |
6 | V- | Output of negative voltage from multiplier unit |
7 | T2OUT | Output of transmitter data (RS-232 levels) |
8 | R2IN | Input of receiver data (RS-232 levels) |
9 | R2OUT | Output of receiver data |
10 | T2IN | Input of transmitter data |
11 | T1IN | Input of transmitter data |
12 | R1OUT | Output of receiver data |
13 | R1IN | Input of receiver data (RS-232 levels) |
14 | T1OUT | Output of transmitter data (RS-232 levels) |
15 | GND | Common output |
16 | VCC | Supply output of voltage source |
MAX232 Circuit Diagram
SMD and DIP Footprint
The MAX232 IC has the following absolute maximum ratings:
· Supply Voltage (VCC): 6V
· Voltage at Any Pin: ±15V
· Storage Temperature: -65°C to +150°C
· Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C (industrial grade)
· Power Dissipation: 500 mW
Exceeding these ratings can damage the IC. Always ensure the device operates within its specified limits for optimal performance and reliability.
MAX232 IC Variants and Packages, Dimensions
Package Type | Pins | Width | Length |
16-DIP | 16 | 0.300" (7.62mm) | 0.600" (15.24mm) |
16-SOIC | 16 | 0.154" (3.90mm) | 0.310" (7.87mm) |
TSSOP-16 | 16 | 0.173" (4.40mm) | 0.500" (12.70mm) |
MAX232 DIP 16: Dual In-line Package. Common for through-hole mounting.
MAX232 SMD 16-SOIC: Small Outline Integrated Circuit. Ideal for surface-mount applications.
TSSOP-16: Thin Shrink Small Outline Package. Use in compact, high-density PCBs.
These are the main MAX 232 package types, with the DIP for through-hole and SOIC/TSSOP for surface-mount designs.
MAX232CPE: 16-pin Plastic DIP package, design for through-hole mounting. Common in older or prototyping circuits.
MAX232EPE: Similar to the MAX232CPE, this 16-pin Plastic DIP, intended for general-purpose, through-hole applications.
MAX232N: Another 16-pin Plastic DIP, offering standard through-hole mounting. A common choice for older designs or when requiring easy manual soldering.
MAX232ESE: 16-pin Narrow SOIC package, 0.154" (3.90mm) width, suitable for surface-mount applications. More compact than the DIP and ideal for high-density boards.
MAX232CSE: A 16-pin Narrow SOIC. This package type is also for surface-mount applications and typically use in space-constrained, modern PCB designs.
MAX232D: A 16-pin SOIC package, 0.154" (3.90mm) width, designed for surface-mount and compact designs, often use in professional and industrial applications.
Each package has different dimensions and mounting options, making the MAX232 versatile for a range of applications, from prototyping (DIP) to high-density PCB designs (SOIC, TSSOP).
MAX232 IC Applications
This IC is versatile and widely used in various applications, including:
Interface Translation: It enables communication between devices that use different voltage levels, such as TTL/CMOS logic (0V to 5V) and RS-232 (±12V). It commonly use in microcontroller-based systems to interface with RS-232 serial devices such as computers and modems.
Multidrop RS-232 Networks: The circuit is ideal for RS-232 networks where multiple devices need to communicate over a shared bus. It allows for the connection of several devices with RS-232 interfaces, ensuring reliable data transmission across the network.
Portable Diagnostics Equipment: Often find the chip in portable diagnostic tools like those used for mobile phone flashing, GPS devices, and set-top boxes. These devices typically require an interface to communicate with computers or other devices via RS-232 connections.
These applications leverage the MAX232's ability to efficiently convert and manage serial communication between different voltage-level systems.
Specifications of MAX232
Parameter | Specification |
Protocol | RS232 |
Number of Drivers/Receivers | 2/2 |
Duplex | Full |
Receiver Hysteresis | 500 mV |
Data Rate | 120Kbps |
Supply Voltage (Vcc) | +4.5V to +5.5V |
Logic Voltage Levels (TTL) | 0V to 5V (or 3.3V for low-voltage designs) |
RS-232 Voltage Levels | ±12V (typically) |
Driver Output Slew Rate | 30V/μs (maximum) |
Receiver Input Voltage Range | ±15V |
Operating Temperature Range | 0°C ~ 70°C |
Storage Temperature Range | -65°C to +150°C |
Power Consumption | 5μW (shutdown mode) |
Power Dissipation | 500 mW (maximum) |
Capacitor Requirement | Typically 1µF for external charge pump capacitors |
Package Types | 16-DIP, 16-SOIC, TSSOP-16, Narrow SOIC16 |
RS-232 Output Impedance | 3.5kΩ (typical) |
Input Resistance | 3kΩ (minimum) |
Output Voltage Swing (RS-232) | ±12V (nominal) |
Receiver Input Capacitance | 5pF (maximum) |
Mounting Type | Surface Mount/ Through Hole |
Structure of the MAX232 IC
This chip is a dual-line driver/receiver designed to convert TTL/CMOS logic levels (0V to 5V) to RS-232 levels (±12V) and vice versa. It features an integrated charge pump that generates the required ±12V from a single +5V supply. The line drivers convert TTL/CMOS signals to RS-232 voltage levels for transmission, while the line receivers convert incoming RS-232 signals back to TTL/CMOS logic levels. The IC also requires external 1µF capacitors to function as charge pumps. Available in packages such as 16-DIP, SOIC-16, and TSSOP-16, the MAX 232 integrates voltage conversion and signal conditioning into a compact, efficient solution for serial communication.
Maxim MAX232 Manufacturer
The IC produce by Maxim Integrated (now part of Analog Devices). It widely available from various distributors, and the circuit use in many embedded systems, microcontroller projects, and serial communication applications.
MAX232 Datasheet PDF:
For detailed specifications, pinouts, application circuits, and electrical characteristics, you can access the pdf datasheet. It provides comprehensive information to guide you in integrating the MAX 232 into your designs.
MAX232 Module Board
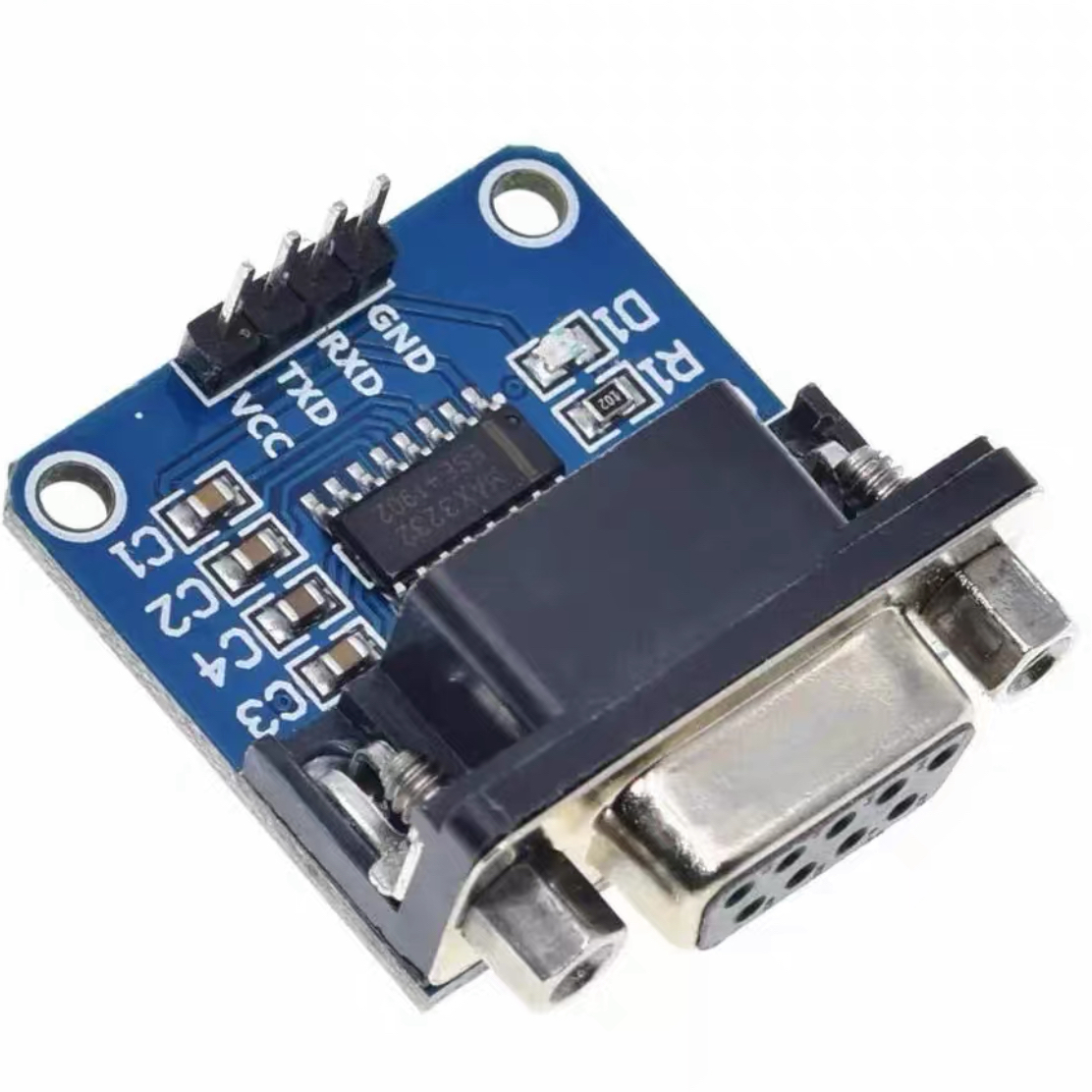

A compact circuit board that integrates the MAX 232 IC or its equivalent, designed to convert RS-232 signals (used by serial communication devices) into TTL/CMOS levels (used by microcontrollers and logic circuits). These boards often include additional components, such as capacitors and connectors, to simplify integration into electronic projects.
MAX232 RS232 to TTL Converter
The RS232 to TTL converter module facilitates communication between devices with RS-232 interfaces (like PCs, modems, and serial peripherals) and devices that operate at TTL levels (such as microcontrollers or development boards). The MAX232 IC use in these converters to shift voltage levels, converting RS-232’s ±12V signals to TTL’s 0V and 5V logic levels, and vice versa.
Applications of MAX 232 Converter Modules
These converter modules widely use in applications like radio modification, where they enable serial communication between radios and microcontrollers. They also use for mobile phone flashing, XBOX360 flashing, GPS data communication, and car diagnostics (OBD-II systems). Other applications include DVD flashing, hard drive repair, and set-top box firmware upgrades. These modules are useful for interfacing RS-232 devices with modern TTL logic systems.
Microcontroller Programming
The MAX232 module use for programming various microcontrollers, including STC, STM32, NXP, and Renesas microcontrollers, by providing an easy interface for serial communication with these devices.
Communication Chip and Voltage
Many of these converter modules use the MAX3232 or similar chips, operating at 3.3V to 5.5V, making them suitable for low-voltage designs. The typical pins on the module include TX (Transmit) for sending data, RX (Receive) for receiving data, VCC (Voltage Supply) for powering the module, and GND (Ground) for a common reference. These modules are useful for serial communication in embedded systems, allowing seamless interaction between microcontrollers and RS-232 devices.
MAX232 vs. Other RS232 Interface Chip MAX3232 IC
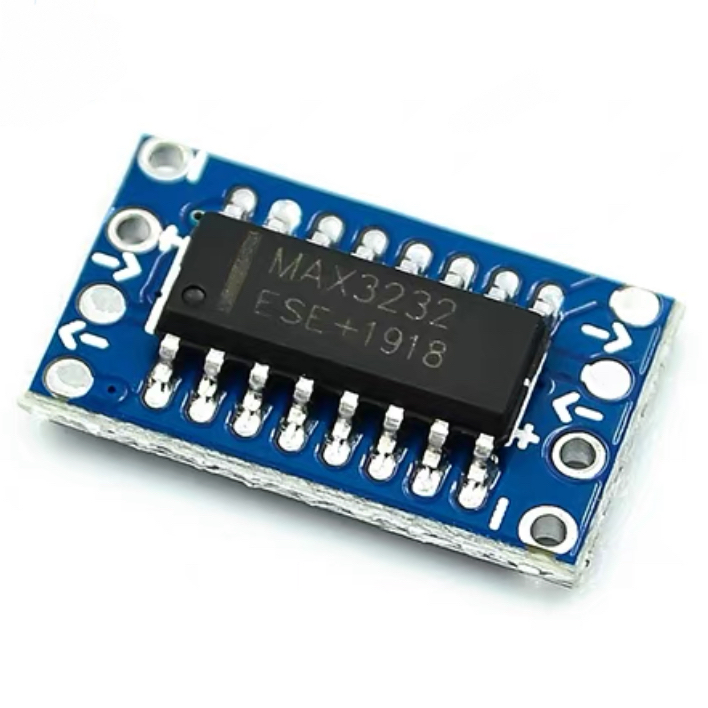

The MAX232 and MAX3232 are both widely used RS-232 interface chips that convert RS-232 voltage levels (±12V) to TTL/CMOS levels (0V to 5V) and vice versa, but they differ in certain aspects.
The MAX 232 operates with a +5V supply and generates the required ±12V using an internal charge pump. It has higher power consumption compared to the MAX3232 as the need for larger external capacitors for voltage conversion. The MAX 232 typically supports data rates up to 250 kbps. It works best in +5V systems, and while it widely use in microcontroller projects, serial communication interfaces, and legacy equipment, it not be suitable for low-voltage designs.
The MAX3232, on the other hand, operates with a +3.3V to +5.5V supply, making it ideal for low-voltage systems. More power-efficient than the MAX 232, making it suitable for battery-powered devices and modern low-voltage embedded systems. Like the MAX232, the MAX3232 supports data rates up to 250 kbps, but it performs better in low-voltage environments. This makes the MAX3232 more versatile for 3.3V systems, which are common in modern microcontroller designs.
The key differences between the two are their operating voltages and power efficiency. The MAX3232 better suite for 3.3V systems and low-power applications, while the MAX232 design for 5V systems or legacy applications.
Frequently Asked Questions[FAQ] about MAX232
What is MAX232 price and where to buy?
The MAX232 typically costs between US$0.50 and US$3.00, depending on the supplier and quantity purchased. Available at electronic component distributors like Orwintech Electronics, often at competitive prices. Bulk purchases offer additional savings, especially for large-scale projects.
What is MAX232 used for?
Primarily used for converting RS-232 signals (±12V) to TTL/CMOS levels (0V to 5V) and vice versa. It enables serial communication between devices with different voltage levels, such as microcontrollers, computers, modems, and other serial peripherals. Often find the MAX 232 in microcontroller-based systems, where it provides an interface between TTL-based microcontrollers and RS-232 devices, making it a key component in many embedded communication projects.
What is the difference between RS-232 and MAX232?
RS-232 is a serial communication standard that defines voltage levels and signaling protocols for data transmission. MAX232, on the other hand, is a voltage level converter that allows communication between TTL/CMOS logic (0V to 5V) and RS-232 (±12V). The MAX 232 converts TTL signals into RS-232 voltage levels, ensuring compatibility between devices that use different voltage signaling standards, such as microcontrollers and serial communication devices.
What is the equivalent of MAX232?
The most common equivalent to the MAX232 is the MAX3232, which also converts RS-232 to TTL. The MAX3232 design to operate at 3.3V to 5.5V supply voltages, making it suitable for low-voltage designs, whereas the MAX-232 typically operates with a +5V supply. Both chips offer similar functionality but differ in voltage compatibility, with the MAX3232 being more suitable for modern 3.3V systems.
How much power does MAX232 use?
The MAX232 consumes little power, typically around 5mA during normal operation when powered by a +5V supply. In shutdown mode, its power consumption drops to 5μW, making it highly efficient in low-power scenarios. The power requirements can vary based on the data rate and the load of the connected devices, but overall, it is a low-power chip that is ideal for embedded systems and portable applications where energy efficiency is crucial.
How to connect MAX232?
To connect the MAX 232, first provide a +5V power supply to the VCC pin and ground to the GND-pin. The RS-232 signals (TX, RX) from the connected device connect to the corresponding Txx (transmit) and Rxx (receive) pins on the MAX232. Require external capacitors (typically 1µF) for the internal charge pump to generate the necessary ±12V for RS-232 communication. The system’s TTL pins connect to the appropriate T/R lines.
What is the maximum data rate supported by the MAX232?
The MAX 232 can support data rates up to 250 kbps (kilobits per second), which is sufficient for most standard RS-232 serial communication applications. This data rate is typical for low to moderate-speed serial interfaces such as computer serial ports, modem connections, and microcontroller communication. However, for higher-speed applications (over 250 kbps), require alternative ICs designed for faster data rates to ensure reliable communication.
What voltage levels are used by the MAX232 for RS-232 communication?
The MAX 232 uses ±12V voltage levels for RS-232 communication, which is the standard voltage range for RS-232 signaling. The positive voltage (V+) typically ranges from +3V to +15V, while the negative voltage (V-) ranges from -3V to -15V. These voltage levels ensure proper signal integrity and long-distance communication, allowing the MAX232 to convert these RS-232 levels into TTL logic levels (0V and 5V) for communication with microcontrollers and other digital devices.
Can the MAX232 be used in low-voltage designs?
The MAX 232 primarily design for +5V systems and not be suitable for low-voltage designs that require 3.3V operation. For low-voltage systems, such as those using 3.3V microcontrollers, the MAX3232 is a better alternative as it operates within the 3.3V to 5.5V range, making it compatible with modern low-voltage systems while still providing reliable RS-232 communication. The circuit not function optimally in 3.3V systems as its higher voltage requirements.
In conclusion, the MAX232 IC is a reliable and efficient solution for bridging the gap between RS-232 devices and TTL/CMOS logic systems. It offers low power consumption, versatility in packaging, and widely use in applications requiring serial communication. Whether you're working with microcontrollers, diagnostic tools, or embedded systems, the MAX232 is a go-to IC for ensuring smooth communication between different voltage level systems.
Read More:
1. MAX485 IC Pinout, Application and MAX485 Module Board
2. 2N3904 Transistor Pinout, Specifications Complete Guide
3. Understanding the TXD2-3V Relay-Features-Applications-and Selection Guide
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog