The MAX485 IC is a low-power, high-speed transceiver designed to handle data communication in RS-485 and RS-422 networks. A versatile and reliable solution commonly use in industrial and communication applications because its robust performance and ease of integration. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about the MAX485 IC, from its features and pinout to applications and frequently asked questions.
3. MAX485 Pinout and Configuration
7. Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]

What is MAX485?
A low-power, half-duplex transceiver used for RS-485 and RS-422 communications. These are differential signaling standards commonly used in industrial data networks, where long-distance communication and high noise immunity are necessary. The MAX485 chip combines a driver and a receiver in single package, offering efficient data transmission over long distances.
Data Rate: The circuit can transmit data at rates up to 2.5 Mbps, making it suitable for high-speed communication in demanding applications.
Low Power Consumption: The IC operates with a supply current between 120µA and 500µA, depending on the load and driver state.
Thermal Shutdown: The ic equips with thermal shutdown circuitry, protecting it from excessive power dissipation by placing the driver outputs into a high-impedance state.
Fail-Safe Receiver: The receiver input has a fail-safe feature that ensures the output is high when the input is open-circuited, helping to maintain reliable communication.
Single 5V Supply: Operate from a single 5V power supply, making it easy to integrate into most digital systems.
Features of MAX485 IC
The circuit supports a common-mode input voltage range from -7V to +12V, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications where signal integrity and noise immunity are critical. It features a 30ns propagation delay and 5ns skew, ensuring fast signal transmission with minimal delay, which is useful for high-speed data communication.
Designed specifically for half-duplex communication, the MAX485 allows bidirectional data flow over the same bus, making it ideal for multi-point communication networks. The IC operates on a single 5 V power supply, simplifying integration into standard systems that use 5V logic.
Can connect up to 32 transceivers on a single bus, providing scalability for complex communication systems. It supports data rates of up to 2.5 Mbps, suitable for fast data transfer in demanding applications. The IC also includes current-limiting and thermal shutdown protection to prevent driver overload and overheating, ensuring long-term reliability.
Both transmitter outputs and receiver inputs protect to ±15kV air ESD, allowing the IC to withstand harsh environments. As a low-power transceiver, the MAX485 is well-suited for battery-powered or power-sensitive devices. Available in 3.3V and 5V variants, offering compatibility with different logic systems.
MAX485 Pinout and Configuration
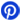
The IC comes in two package options, including DIP (Dual In-line Package) and SO (Small Outline) configurations. Below is a breakdown of the pinout for both the DIP and SO packages:
MAX485 Pin Description DIP Package Pinout
Pin No. | Pin Name | Description |
1 | RO | Receiver Output: If A > B by 200mV, RO is high; If A < B by 200mV, RO is low. |
2 | RE | Receiver Output Enable: RO is enabled when RE is low; high impedance when RE is high. |
3 | DE | Driver Output Enable: The driver outputs, Y and Z, are enabled when DE is high. High impedance when DE is low. |
4 | DI | Driver Input: Low on DI forces Y low and Z high. High on DI forces Y high and Z low. |
5 | GND | Ground |
6 | A | Non-inverting Receiver Input and Driver Output |
7 | B | Inverting Receiver Input and Inverting Driver Output |
8 | VCC | Positive Supply: 4.75V ≤ VCC ≤ 5.25V |
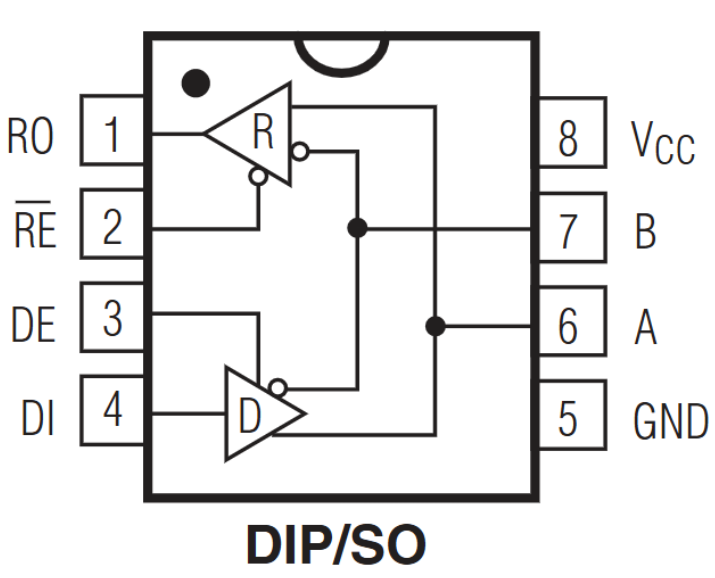
uMAX SO Package Pinout
Pin No. | Pin Name | Description |
1 | B | Inverting Receiver Input and Inverting Driver Output |
2 | VCC | Positive Supply: 4.75V ≤ VCC ≤ 5.25V |
3 | RO | Receiver Output: If A > B by 200mV, RO is high; If A < B by 200mV, RO is low. |
4 | RE | Receiver Output Enable: RO is enabled when RE is low; high impedance when RE is high. |
5 | DE | Driver Output Enable: The driver outputs, Y and Z, are enabled when DE is high. High impedance when DE is low. |
6 | DI | Driver Input: Low on DI forces Y low and Z high. High on DI forces Y high and Z low. |
7 | GND | Ground |
8 | A | Non-inverting Receiver Input and Driver Output |
MAX485 Circuit Diagram
A basic circuit connects the IC between a microcontroller (TTL level) and an RS-485 bus. The DI pin connects to the microcontroller’s TX pin, and the RO pin connects to RX. The DE and RE pins control data direction—usually tied together and connected to a GPIO pin. The A and B pins connect to the differential RS-485 bus lines, with a 120Ω termination resistor across A and B for signal integrity.
Description of MAX485 Chip
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Voltage (VCC): -0.3V to +6V
Input Voltage (A, B): -8V to +13V
Logic Input Voltage (DI, DE, RE): -0.3V to +6V
Receiver Output Voltage (RO): -0.3V to (VCC + 0.3V)
Continuous Power Dissipation: 500 mW (DIP), 450 mW (SO)
Operating Temperature Range: 0°C to +70°C
Storage Temperature Range: -65°C to +150°C
MAX485 Typical Circuit
Include the IC connected to a microcontroller or UART interface. The DI pin receives data from the MCU’s TX pin, and the RO-pin sends data to the MCU’s RX pin. The DE and RE pins control transmit and receive modes. The A and B pins connect to the twisted-pair RS-485 bus with a 120Ω termination resistor across them to prevent reflections.
Package Dimensions
MAX485 DIP Package: Standard 8-pin Dual In-line Package (DIP-8) with 2.54mm pin spacing, suitable for through-hole applications and easy prototyping.
MAX485 SMD Package: Compact 8-pin Small Outline (SOIC-8) surface-mount, ideal for PCB designs requiring smaller footprints and automated assembly.
Manufacturer: Maxim MAX485
The IC manufacture by Maxim Integrated, a leading semiconductor company known for producing high-performance analog and mixed-signal integrated circuits. The MAX485 is part of Maxim’s RS-485/RS-422 transceiver family, designed for robust, low-power, and high-speed data communication.
Maxim Integrated (now part of Analog Devices, Inc.) ensures that the MAX485 meets strict industry standards for signal integrity, electrostatic discharge protection, and thermal reliability. The IC is available in multiple package types (DIP-8 and SOIC-8) and widely use in industrial control systems, automation, sensor networks, and serial data communication applications.
MAX485 Module Board
MAX485 RS485 Transceiver Module
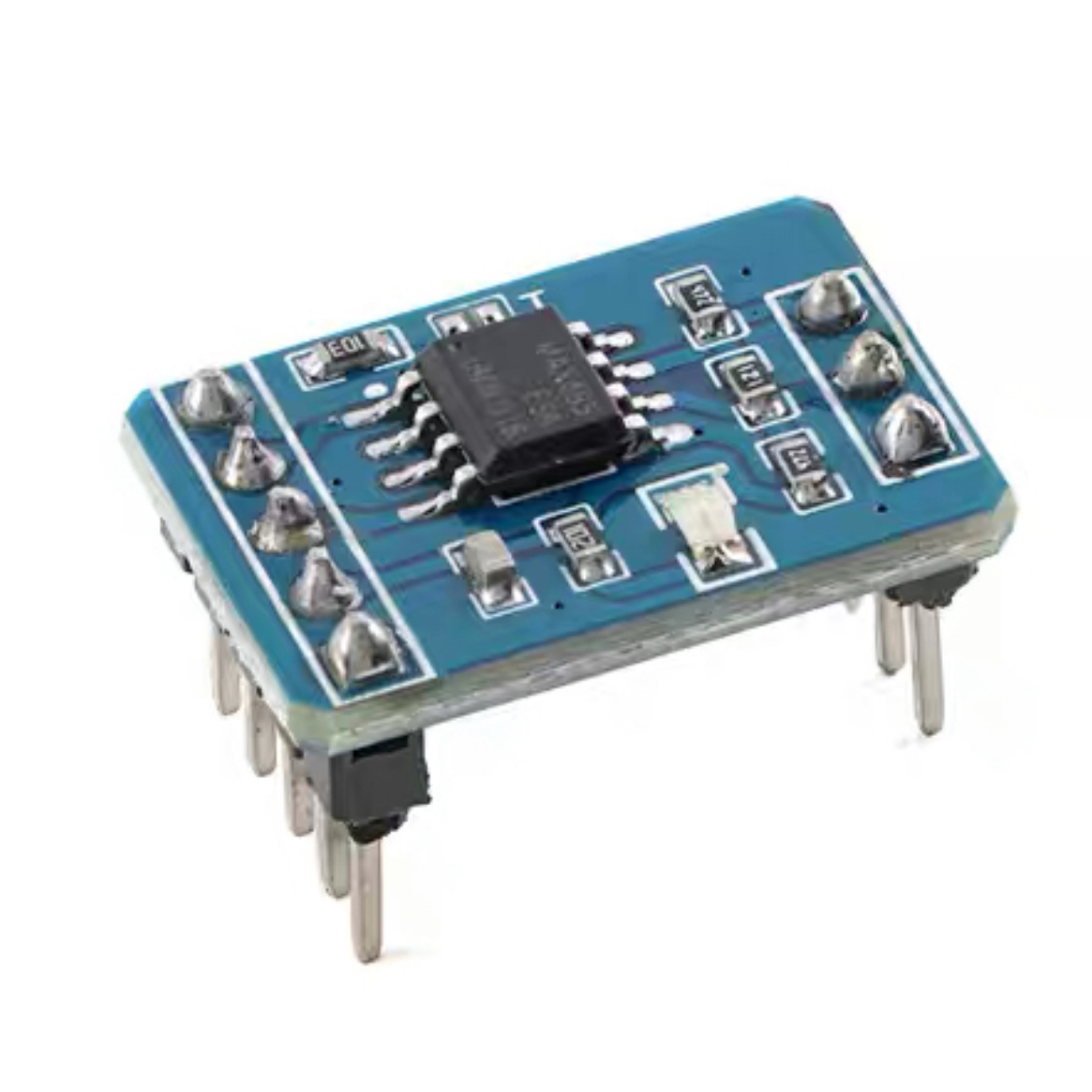

The transceiver module is a compact communication interface board built around the MAX485 IC. It serves as a TTL to RS-485 signal converter, allowing microcontrollers and other TTL-based devices to communicate over long distances using the RS-485 differential signaling standard.
This module converts TTL serial signals (TX/RX) from microcontrollers such as Arduino, ESP32, or STM32 into RS-485 differential signals, enabling reliable, noise-resistant communication across distances up to 1200 meters. It also supports bidirectional communication, making it suitable for half-duplex systems.
The board includes serial port pins for easy connection to a microcontroller and direction control pins (DE/RE) to switch between transmit and receive modes. Additionally, it features a 120-ohm termination resistor across the A and B lines to maintain signal integrity and prevent reflections in long-distance networks.
Use for reliable long-distance serial communication in industrial and embedded systems. Common applications include industrial automation, smart energy meters, building management systems, security and access control, remote data acquisition (SCADA), and Modbus or DMX512 networks. Also popular in Arduino and Raspberry Pi projects for adding RS-485 communication capability.
5V MAX485 TTL to RS485 Converter Module
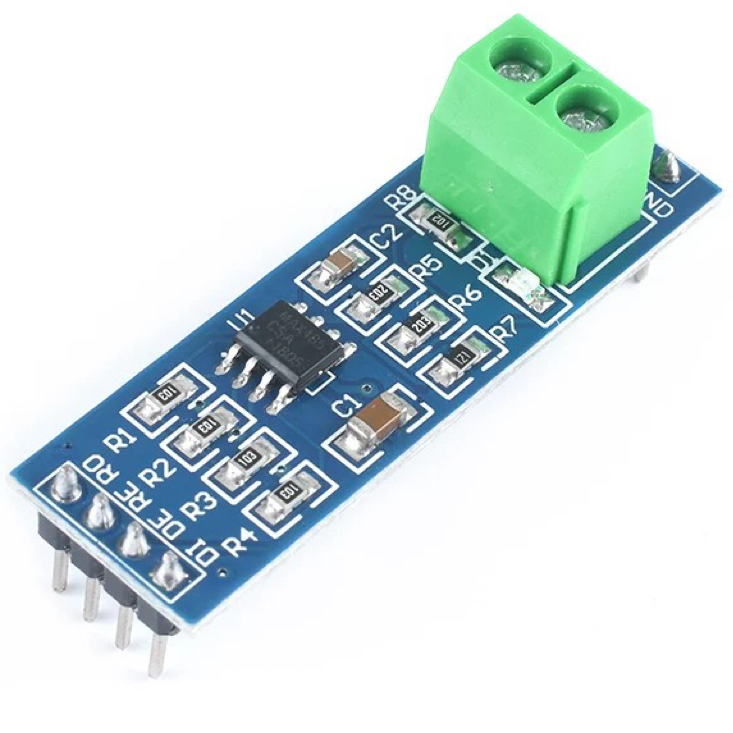
The 5 V converter module uses the MAX485 chip as a low-power transceiver for reliable RS-485 communication. It converts TTL serial signals from microcontrollers (such as Arduino, STM32, or ESP32) into RS-485 differential signals for long-distance data transmission.
All pins of the MAX485 bring out on the module, allowing full control of transmit and receive modes. It operates at 5V, supports half-duplex communication, and measures 44 × 14 mm, making it compact and easy to integrate into embedded projects.
This module use for long-distance, noise-resistant serial communication in embedded systems. Common applications include Arduino and microcontroller projects, industrial automation, SCADA and sensor networks, Modbus communication, and building management systems.
MAX485 Application
The IC is a versatile and reliable transceiver designed for bidirectional data communication over multipoint bus transmission lines. Its robust differential signaling, low power consumption, and high-speed performance make it an ideal choice for applications requiring long-distance and noise-resistant communication.
One of the primary uses of the circuit is as a low-power RS-485 transceiver, where it enables multiple devices to communicate over a shared bus in industrial automation systems, sensor networks, and factory monitoring applications. It can also function as a low-power RS-422 transceiver, providing similar differential signaling capabilities for point-to-point or multipoint networks.
The IC can act as a level translator, converting logic-level TTL signals from microcontrollers or other digital devices into RS-485 or RS-422 differential signals for reliable long-distance transmission. This makes it highly suitable for microcontroller projects, embedded systems, and communication between devices with different voltage levels.
In addition, the chip design for EMI-sensitive applications. Its differential signaling reduces susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, ensuring data integrity in noisy industrial environments. Commonly use in industrial-control local area networks, including SCADA systems, building management systems, and automated production lines.
Typical applications of the IC include Arduino and microcontroller-based RS-485 networks, Modbus communication systems, remote data acquisition, sensor interfacing, and long-distance serial communication in both commercial and industrial projects. Its half-duplex design allows multiple devices to share the same communication line efficiently, making it suitable for multipoint communication networks where multiple nodes must transmit and receive data reliably.
In summary, the MAX485 is a highly flexible transceiver IC that excels in low-power, high-speed, and long-distance communication applications, offering robust performance for both industrial and embedded system networks.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
What is MAX485 price?
The pricing of IC varies depending on the supplier, quantity, and region. Typically, a single MAX485 costs around US$0.08 to US$0.5, while bulk purchases can reduce the price significantly. Modules based on the MAX485, such as TTL to RS-485 converters, cost slightly more as additional components and PCB assembly. The IC is available from online electronics stores like Orwintech Electronics, making it an affordable option for both hobbyists and industrial applications.
What is MAX485 alternative/equivalent?
Several ICs can serve as alternatives or equivalents to the MAX 485. Common choices include the SN75176, SN65HVD1785, and LT1785, which offer similar RS-485/RS-422 transceiver functions with low power consumption and half-duplex operation. These alternatives provide comparable data rates, fail-safe inputs, and thermal protection, making them suitable for industrial and embedded projects. Selection depends on operating voltage, package type, data rate requirements, and availability. Many microcontroller-based RS-485 networks use these ICs interchangeably with the MAX485.
What is MAX485 circuit example?
A typical MAX 485 circuit connects the IC between a microcontroller and an RS-485 bus. The microcontroller’s TX pin connects to the DI-pin of the MAX485, and RX connects to RO. The DE and RE pins control direction, often tied together to a GPIO-pin. The A and B pins connect to the differential RS-485 bus with a 120-ohm termination resistor between them. This setup enables half-duplex communication, converting TTL signals to RS-485 signals and back, allowing reliable long-distance data transmission.
What is the use of MAX485?
The IC use for long-distance, noise-resistant data communication in industrial and embedded systems. It converts TTL-level signals from microcontrollers into RS-485 differential signals and vice versa. This allows multiple devices to communicate over a shared bus in a half-duplex configuration. Typical applications include industrial automation, sensor networks, SCADA systems, building management, and embedded microcontroller projects. Its low-power design, fail-safe receiver, and EMI immunity make it reliable for multi-node networks and harsh operating environments.
What is the difference between MAX485 and MAX485E?
The MAX485E is an enhanced version of the standard MAX485. While both are low-power RS-485 transceivers, the MAX485E features lower supply current, improved thermal performance, and slightly better electrical characteristics. It also have enhanced fail-safe input features for open or idle buses. Functionally, both ICs support half-duplex communication and similar data rates, but prefer the MAX485E in energy-sensitive or temperature-critical applications where reduced power consumption and slightly better performance are advantageous.
What types of communication does the MAX485 support?
The MAX 485 supports half-duplex RS-485 communication and RS-422 point-to-point connections. In half-duplex RS-485, multiple devices share the same differential bus for bidirectional communication, making it suitable for multi-node networks. RS-422 operation allows differential signaling between two devices, providing high-speed, noise-resistant data transmission. The IC converts TTL-level serial signals to differential signals for long-distance communication, making it ideal for industrial automation, building management, SCADA systems, and embedded microcontroller projects requiring robust serial communication.
Is MAX485 fail safe?
Yes, the MAX485 includes a fail-safe receiver. When the differential input is open-circuit, shorted, or idle, guarantee the receiver output to stay high, preventing false zero readings on the bus. This feature is key in industrial and multi-node communication networks, where accidental disconnections, floating lines, or interference can otherwise cause unreliable data. The fail-safe mechanism ensures that devices connected to the RS-485 bus maintain a predictable logic state, improving the reliability and safety of data transmission.
What is the speed of MAX485?
The MAX 485 IC supports data rates of up to 2.5 Mbps, making it suitable for high-speed serial communication over RS-485 or RS-422 networks. Its low propagation delay (30ns) and minimal skew (5ns) ensure that signals remain synchronized across multiple devices. While can achieve the maximum speed over short distances, longer cable runs require lower speeds to maintain signal integrity. This high-speed capability allows to use the circuit in applications such as industrial automation, real-time monitoring, and embedded communication networks.
What is the maximum distance for MAX485?
The MAX 485 can reliably transmit data over distances of up to 1200 meters (approximately 4000 feet) at lower data rates. The maximum distance depends on cable type, signal rate, and environmental noise. For higher speeds, the effective distance decreases as signal attenuation and reflections. Proper termination resistors (typically 120Ω) and twisted-pair cables help maintain signal integrity over long distances. This capability makes the circuit ideal for industrial networks, building automation, and multi-point RS-485 communication systems.
Conclusion
The MAX485 is an key IC for anyone working with RS-485 or RS-422 communication systems. Its low power consumption, high-speed data transmission, and robustness make it ideal for industrial, networking, and communication applications. Whether you're designing a long-distance data network or creating a noise-resistant industrial control system, the MAX485 offers a reliable and cost-effective solution for your needs.
Read More:
1. 2N3904 Transistor Pinout, Specifications Complete Guide
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog