The LM393 is a dual comparator IC that offers high precision and low power consumption, making it ideal for a variety of applications across consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial devices. Manufactured by leading companies such as ON Semiconductor, Texas Instruments (TI), and STMicroelectronics, the LM393 delivers excellent performance with a wide supply voltage range and low input offset voltage. In this blog, we’ll dive into the LM393's features, pinout, applications, and how you can integrate this versatile component into your next project.
2. LM393 Pinout, CAD Model, Circuit Diagram
4. Dual Comparator IC LM393 Technical Specifications
5. LM393 Equivalent and Replacement
10. Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ] about IC Chip LM393

What is LM393?
The LM393 is a dual independent precision voltage comparator IC designed for both single and split supply operation. It features low input offset voltage as low as 2.0 mV, ensuring high accuracy in voltage comparison tasks. With a wide common mode input voltage range, including ground, it can operate effectively in a variety of systems. The circuit commonly use in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and industrial circuits for tasks such as signal comparison and amplification. Its precision and flexibility make it a go-to solution for applications requiring reliable and accurate voltage threshold detection.
LM393 Pinout, CAD Model, Circuit Diagram
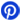
Pin No | Pin Name | Description |
1 | OUT1 | Output of the first comparator. Requires a pull-up resistor for proper operation. |
2 | IN1- | Inverting input of the first comparator. The voltage to compare against the reference is applied here. |
3 | IN1+ | Non-inverting input of the first comparator. This connect to the reference voltage or signal. |
4 | Vcc- | Negative supply pin. For single-supply, connect to ground, and for dual-supply, connect to the negative voltage. |
5 | IN2+ | Non-inverting input of the second comparator. Similar to IN1+, this is where apply the reference voltage for the second comparator. |
6 | IN2- | Inverting input of the second comparator. Apply the signal to compare here. |
7 | OUT2 | Output of the second comparator. Also requires a pull-up resistor for proper logic-level operation. |
8 | Vcc+ | Positive supply pin. Connect to the positive supply voltage, either single or dual-supply configuration. |
This pinout commonly use in SMD packages such as TSSOP, SOIC, and DFN, and differ in layout for through-hole versions like DIP-8.
CAD Model

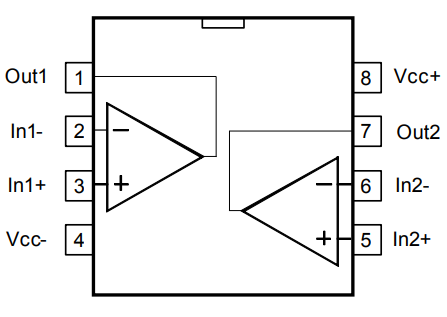
Circuit Schematic Diagram
LM393 Comparator Features
The chip is a highly versatile dual comparator IC that boasts several features making it ideal for precision voltage comparison applications. Here’s a breakdown of its key characteristics:
Wide Supply Voltage Range: Can operate with a single supply voltage from 2V to 36V or with dual supplies ranging from ±1V to ±18V, making it adaptable to a wide range of circuit configurations.
Low Supply Current: It has a low quiescent current of just 0.45 mA, independent of the supply voltage, translating to 1 mW per comparator at 5V. This makes it highly efficient, particularly in battery-powered applications.
Low Input Bias Current: The input bias current is as low as 20 nA typical, helping to minimize errors in precision applications.
Low Input Offset Current: With an offset current of ±3 nA, the circuit ensures minimal voltage difference between inputs, further enhancing its accuracy.
Low Input Offset Voltage: The ±1 mV typical input offset voltage means minimal deviation from the ideal comparator behavior, making it highly suitable for precision circuits.
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range: The chip features an input common-mode voltage range that includes ground, which means it can work with single-supply operation without requiring a negative rail.
Low Output Saturation Voltage: The output saturation voltage is 80 mV typ. when sinking 4 mA, ensuring reliable logic-level output.
Differential Input Voltage Range: The input differential voltage range is equal to the supply voltage, allowing for the full swing of voltage comparison.
Logic-Compatibility Outputs: Compatible with TTL, DTL, ECL, MOS, and CMOS logic families, providing flexibility when interfacing with different logic circuits.
Package Options: The component is available in a variety of package types, including DFN8 2x2, MiniSO8, TSSOP8, SO8 and DIP8, providing options for both through-hole and surface-mount designs.
ESD Protection: The LM393W variant includes internal ESD protection (up to 2 kV HBM), ensuring robustness in environments with electrostatic discharge risk.
These features combine to make the chip an excellent choice for many applications in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial circuits that require precision voltage comparison with minimal power consumption and high reliability.
Dual Comparator IC LM393 Technical Specifications
Specification | Value |
Supply Voltage (Single Supply) | 2V to 36V |
Supply Voltage (Dual Supply) | ±1V to ±18V |
Supply Current (Quiescent) | 0.45 mA per comparator (typical) |
Power Consumption | 1 mW per comparator at 5V |
Input Bias Current | 20 nA (typical) |
Input Offset Current | ±3 nA (typical) |
Input Offset Voltage | ±1 mV (typical) |
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range | Includes Ground |
Output Saturation Voltage | 80 mV typ. at Isink = 4 mA |
Differential Input Voltage Range | Equal to Supply Voltage |
Output Compatibility | TTL, DTL, ECL, MOS, CMOS compatible |
Package Options | DFN8 2x2, MiniSO8, TSSOP8, SO8, DIP8 |
Operating Temperature | 0°C ~ 70°C |
Mounting Type | Surface Mount, Through-Hole |
LM393 Manufacturers
The dual comparator IC produce by several well-known manufacturers in the semiconductor industry. Here are the primary manufacturers:
ON Semiconductor
ON-SEMI is one of the major producers of the LM 393 and offers various variants with high-quality standards and applications, including automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics.
Texas Instruments (TI)
Texas Instruments (TI) manufactures the circuit with a reputation for reliability, precision, and performance in various fields such as consumer devices, signal processing, and measurement systems.
STMicroelectronics
ST also produces this component, focusing on delivering affordable, high-performance comparators that meet the needs of industrial electronics, automotive systems, and consumer applications.
These manufacturers ensure that the circuit maintains consistent quality and availability across different markets, providing a reliable choice for voltage comparison and signal conditioning applications.
LM393 Package Details
The dual comparator IC is available in a variety of packages, catering to both Surface-Mount Device (SMD) and Through-Hole configurations. Here are the package details:
LM393 SMD (Surface-Mount Device) Packages:
DFN8 2x2

Dimensions: 2.0 mm x 2.0 mm. A small 8-pin package, perfect for high-density designs with space constraints, offering easy integration into modern surface-mount technology (SMT) applications.
MSOP-8
Dimensions: 0.118" (3.00 mm) width. A compact 8-pin Mini Small Outline Package that reduces the footprint while maintaining the functionality of traditional SOIC packages.
TSSOP-8

Dimensions: 0.173" (4.40 mm) width. The Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP) with 8 pins; it offers a thin profile, making it ideal for space-sensitive applications while providing high-performance characteristics.
8-SOIC
Dimensions: 0.154" (3.90 mm) width. Description: A Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC) with 8 pins, widely used in industrial and consumer electronics, offering a compact footprint for surface-mount assembly.
Through-Hole Package:
DIP-8 (Dual In-line Package)

Dimensions: 0.300" (7.62 mm) width. The classic 8-pin Through-Hole Package with 0.3-inch lead spacing, ideal for traditional circuit boards and manual assembly or prototyping.
These package options provide flexibility in design, from small and thin packages suitable for SMT to the classic DIP package for through-hole mounting. The component can use across a broad range of applications, offering performance and reliability in compact and traditional designs alike.
LM393 Datasheet PDF
LM393 Equivalent and Replacement
The LM393 is a popular dual comparator IC, but several other comparators from different manufacturers offer similar functionality and can serve as equivalents or replacements. Here's a list of some of the most common equivalents:
Equivalent IC | Manufacturer | Description |
LM358 | Texas Instruments | Dual operational amplifier with comparator functionality, commonly used in signal processing and conditioning. |
TL082 | Texas Instruments | Dual JFET input operational amplifier, often used for general-purpose amplification and comparison tasks. |
LM311 | Texas Instruments | A single comparator with similar specifications; can use as a replacement in circuits requiring just one comparator. |
LM193 | Texas Instruments | Dual comparator IC with similar features but with different input characteristics, suitable for precision applications. |
LM293 | ON Semiconductor | Dual comparator with a broader voltage range and low-power characteristics, often used in industrial and automotive applications. |
LM2903 | ST Microelectronics | Dual comparator with an extended operating temperature range, making it ideal for automotive and industrial environments. |
These equivalents offer similar features such as low offset voltage, low power consumption, and wide supply voltage range. However, depending on the specific needs of your application, you might need to review other aspects like input bias current, temperature range, or output type before selecting a replacement.
Key Considerations for Replacements:
Package Compatibility: Ensure that the equivalent is available in the package format suitable for your design (e.g., DIP-8, SOIC-8).
Performance Specs: Although these parts are functionally similar, verify their input offset voltage, supply current, and temperature range to ensure they meet your circuit requirements.
Manufacturer Availability: Different manufacturers may offer unique variants with specific enhancements (e.g., LM393W with ESD protection).
How to Use LM393
Using the comparator is relatively simple. The main components involved are the comparator IC itself, a reference voltage, resistors for the voltage divider, and a pull-up resistor for the output. Here's how you can set up a basic comparator circuit:
1. Connect the non-inverting input of the LM393 to the signal you want to compare.
2. Connect the inverting input to a reference voltage (this can create using a voltage divider or a precision voltage source).
3. Attach a pull-up resistor (usually 10kΩ to 100kΩ) to the output pin of the LM393, as the output is an open collector.
4. Power the circuit using a suitable voltage source, either single or dual supply.
The output of the LM393 will switch between low and high based on whether the input signal is above or below the reference voltage.
LM393 Application
The dual comparator IC commonly use in a variety of applications for voltage comparison, signal conditioning, and threshold detection. Here are some key applications:
Voltage Monitoring and Level Detection:
Can compare an input signal against a reference voltage. If the signal crosses a specific threshold, it triggers a high or low output, making it ideal for voltage monitoring, overvoltage protection, and battery level detection.
Zero-Crossing Detection:
Frequently use in zero-crossing detection circuits, where it detects the point where an AC signal crosses zero volts. This commonly use in phase-locked loops (PLLs), frequency counters, and AC signal processing.
Temperature Sensing:
By using a temperature sensor (e.g., thermistor or thermocouple) as the input signal, the circuit can use in temperature monitoring systems. It compares the sensor's output against a reference voltage to turn on/off a cooling or heating system when reach a preset temperature threshold.
Signal Shaping and Filtering:
Used in circuits to clean up noisy signals and provide a clean, sharp output based on voltage comparisons. Used in pulse generation, PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), and signal waveform shaping.
Comparator in Logic Systems:
Widely use in digital logic circuits, where it acts as a voltage comparator to provide logical high/low outputs, especially in systems that need to compare analog signals and convert them into digital logic levels.
Overcurrent Protection:
It can compare the current sensor output against a reference voltage to protect circuits from overcurrent situations. When the current exceeds a threshold, the chip triggers an action (e.g., activating a relay to shut off the circuit).
Automotive and Industrial Applications:
In automotive systems, the circuit can use for fuel level sensing, voltage regulation, and current detection. In industrial automation, it can monitor and trigger alarms or actuators based on various sensor inputs.
LM393 Module
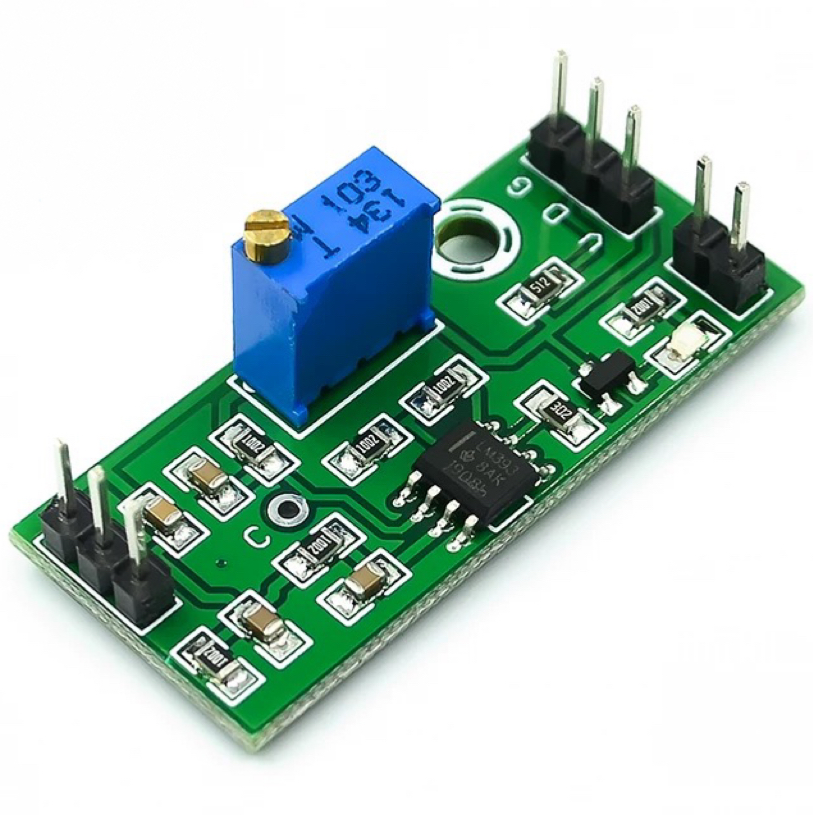
LM393 3.5-24V Voltage Comparator Module High Level Output Analog Control With LED Indicator
The voltage comparator module design for precision signal comparison and waveform shaping in various electronic applications. This module typically includes:
Adjustable Potentiometer: Used to generate a reference voltage for comparison.
Dual High-Level Output: Provides two outputs for low and high-level logic signals based on the comparison.
LED Indicator: Shows the output status visually, indicating whether the input voltage is above or below the reference voltage.
In operation, the voltage from the sensor or voltage divider resistors compare against the reference voltage. If the input exceeds the reference, the output switches to a low or high state, depending on the configuration. This module can used for voltage monitoring, threshold detection, or signal conditioning tasks in embedded systems, automation, and control circuits.
LM358 vs LM393
Specification | LM358 | LM393 |
Manufacturer | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, STMicroelectronics |
Package / Case | SOIC-8, DIP-8, TSSOP-8, MSOP-8 | SOIC-8, DIP-8, TSSOP-8, DFN8 2x2, MiniSO8 |
Number of Pins | 8 | 8 |
Input Offset Voltage (Vos) | ±3 mV (typical) | ±1 mV (typical) |
Supply Voltage | 3V to 32V (Single), ±1.5V to ±16V (Dual) | 2V to 36V (Single), ±1V to ±18V (Dual) |
Quiescent Current | 1.2 mA (typical) | 0.45 mA (per comparator, typical) |
Current - Input Bias (Max) | 200 nA (typical) | 20 nA (typical) |
Lead Free | Yes | Yes |
Key Differences:
Input Offset Voltage (Vos): The LM393 has a lower Vos (±1 mV) more suitable for high-precision applications compared to the LM358 (±3 mV).
Supply Voltage: The LM393 supports a wider supply voltage range (2V to 36V) compared to the LM358 (3V to 32V), giving it more flexibility.
Voltage Gain: The LM358 is an operational amplifier with a high voltage gain (typically 100 dB), while the LM393 is a voltage comparator, so it doesn't have a voltage gain specification.
Quiescent Current: The LM393 has a lower quiescent current (0.45 mA) per comparator, making it more power-efficient compared to the LM358 (1.2 mA).
Input Bias Current: The LM393 has a much lower input bias current (20 nA) compared to the LM358 (200 nA), which helps minimize errors in precise applications.
The LM393 typically use for voltage comparison tasks, while the LM358 is a dual operational amplifier suited for signal amplification and conditioning.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ] about IC Chip LM393
What is LM393 price?
The LM393 typically costs between $0.20 to $1.50 per unit, depending on the manufacturer and quantity purchased. Prices can vary based on the package type (e.g., DIP, SOIC, TSSOP) and supplier, with bulk purchases often offering lower prices.
What is LM393 used for?
The LM393 used as a voltage comparator in electronic circuits. It compares an input voltage with a reference voltage, outputting a low or high signal based on the comparison. Common applications include voltage monitoring, signal conditioning, temperature sensing, and threshold detection in consumer, industrial, and automotive systems.
Can the LM393 operate with a single supply?
Yes, the LM393 can operate with a single supply voltage as low as 2V. It also works with dual supply voltages, providing flexibility in design. The input common-mode voltage range includes ground, allowing the IC to function effectively with a single supply without needing a negative rail.
Does the LM393 require a pull-up resistor?
Yes, the LM393 has an open-collector output, meaning it requires a pull-up resistor to generate a proper logic level output. The resistor pulls the output to a high voltage when the comparator output is inactive (low). Typical values for the pull-up resistor range from 10kΩ to 100kΩ.
What is the equivalent of LM393?
Have several equivalents, including the LM358, TL082, LM311, LM193, LM293, and LM2903. These comparators share similar electrical characteristics, such as low input offset voltage and wide supply voltage ranges, but differ in packaging, input bias current, and other specifications.
What is the difference between LM393 and LM339?
The both are dual-comparators, but the LM393 has two comparators in a single package, while the LM339 has four comparators. Additionally, the LM393 has a lower input offset voltage and often use in more precision-based applications, whereas the LM339 typically use for general-purpose voltage comparison.
What frequency is LM393 best used at?
The LM393 is best used at low frequencies, typically up to a few hundred kHz. Its performance may degrade at higher frequencies because the limited slew rate and response time. Ideal for low-speed applications, such as signal comparison, threshold detection, and zero-crossing detection.
What is the voltage range LM393 can handle?
The LM393 can handle a single supply voltage ranging from 2V to 36V or a dual supply range of ±1V to ±18V. This wide voltage range allows it to use in a variety of designs, from low-voltage battery-operated systems to higher-voltage industrial applications.
Conclusion
The LM393 is a highly effective dual comparator IC, ideal for a wide range of applications, including voltage comparison, signal conditioning, and threshold detection. With its low power consumption, excellent precision, and flexibility in supply voltage, it continues to be a go-to choice for many electronics projects, from consumer to industrial electronics. Whether you’re building a voltage monitor or a signal processing circuit, this circuit offers a reliable and efficient solution.
Read More:
1. MAX485 IC Pinout, Application and MAX485 Module Boar
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
What is 100 Ohm Resistor And Color Code?

100 ohm resistor color code
2025-05-17








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog